Give the name of one or more polysaccharides that matches each of the following descriptions:
a. not digestible by humans

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

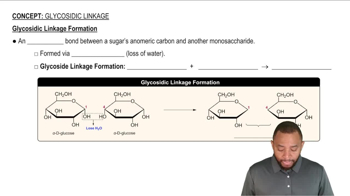
Give the name of one or more polysaccharides that matches each of the following descriptions:
a. not digestible by humans
Give the name of one or more polysaccharides that matches each of the following descriptions:
c. contains only α(1→4)-glycosidic bonds
Give the name of one or more polysaccharides that matches each of the following descriptions:
b. the storage form of carbohydrates in plants
Give the name of one or more polysaccharides that matches each of the following descriptions:
d. produces maltose during digestion
Isomaltose, obtained from the breakdown of starch, has the following Haworth structure:
a. Is isomaltose a mono-, di-, or polysaccharide?
Isomaltose, obtained from the breakdown of starch, has the following Haworth structure:
b. What are the monosaccharides in isomaltose?