Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula if cyclic, for each of the following:
c. 2,3-dichloro-1-butene

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula if cyclic, for each of the following:
c. 2,3-dichloro-1-butene
Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following:
b. 2,5-dibromophenol
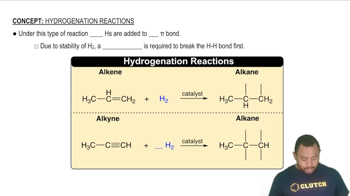
Give the name for the product from the hydrogenation of each of the following:
a. 3-methyl-2-pentene
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula for the product of each of the following:
a.
Draw the condensed structural formulas for all the possible alkane isomers that have a total of six carbon atoms and a four-carbon chain.
Draw the condensed structural formulas for all the possible haloalkane isomers that have four carbon atoms and a bromine.