Textbook Question
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
c.

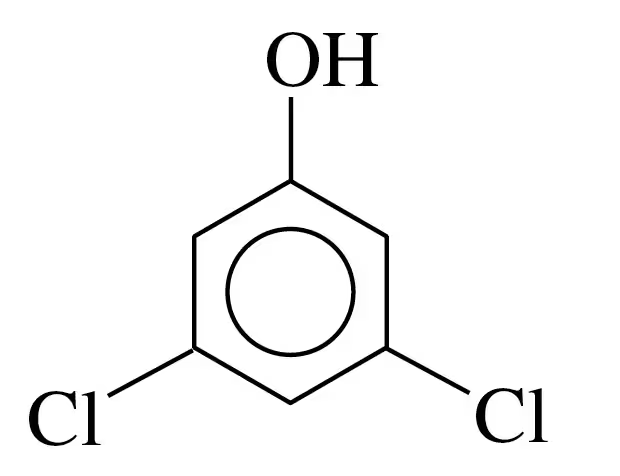
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
c.
Draw the structural formula for the product in each of the following reactions:
d.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
b.
Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds:
c. 4-ethyltoluene
Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds:
c. 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene
Write the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of each of the following hydrocarbons found in gasoline:
c. 3-ethyltoluene