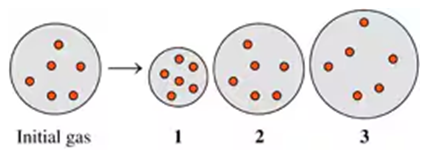
Two flasks of equal volume and at the same temperature contain different gases. One flask contains 5.0 g of O2 and the other flask contains 5.0 g of H2. Is each of the following statements true or false? Explain.
b. The pressures in the flasks are the same.