In certain lung ailments such as emphysema, there is a decrease in the ability of oxygen to diffuse into the blood.
b. Why does a person with severe emphysema sometimes use a portable oxygen tank?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


In certain lung ailments such as emphysema, there is a decrease in the ability of oxygen to diffuse into the blood.
b. Why does a person with severe emphysema sometimes use a portable oxygen tank?
Using the answer from problem 8.61, how many grams of nitrogen are in Whitney's lungs at STP if air contains 78% nitrogen?
Two flasks of equal volume and at the same temperature contain different gases. One flask contains 5.0 g of O2 and the other flask contains 5.0 g of H2. Is each of the following statements true or false? Explain.
b. The pressures in the flasks are the same.
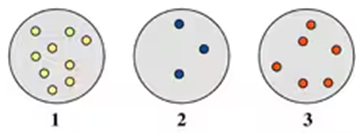
Indicate which diagram (1, 2, or 3) represents the volume of the gas sample in a flexible container when each of the following changes (a to d) takes place:
c. Atmospheric pressure decreases if temperature does not change.
Indicate which diagram (1, 2, or 3) represents the volume of the gas sample in a flexible container when each of the following changes (a to d) takes place:
d. Doubling the atmospheric pressure and doubling the Kelvin temperature.
A balloon is filled with helium gas with a partial pressure of 1.00 atm and neon gas with a partial pressure of 0.50 atm. For each of the following changes (a to e) of the initial balloon, select the diagram (A, B, or C) that shows the final volume of the balloon:
<IMAGE>
c. All of the neon gas is removed (T and P do not change).