Draw the line-angle formula and write the IUPAC name for each of the following:
a. A carboxylic acid that has the formula C6H12O2, with no substituents

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Draw the line-angle formula and write the IUPAC name for each of the following:
a. A carboxylic acid that has the formula C6H12O2, with no substituents
Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
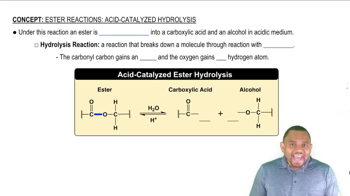
<IMAGE>
a. Draw the condensed structural formula for propyl acetate.
Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
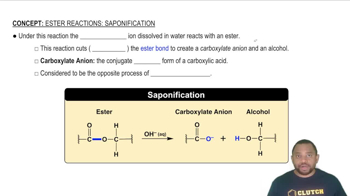
<IMAGE>
b. Write the balanced chemical equation for the formation of propyl acetate.
Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
<IMAGE>
e. How many milliliters of a 0.208 M NaOH solution is needed to completely hydrolyze (saponify) 1.58 g of propyl acetate?
Ethyl octanoate is a flavor component of mangoes.
<IMAGE>
c. Write the balanced chemical equation for the acid hydrolysis of ethyl octanoate.
Ethyl octanoate is a flavor component of mangoes.
<IMAGE>
e. How many milliliters of a 0.315 M NaOH solution is needed to completely hydrolyze (saponify) 2.84 g of ethyl octanoate?