Which compound in each of the following pairs would be more soluble in water? Explain.
c. butanal or hexanal

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones Problem 28b
Problem 28b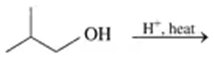
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Which compound in each of the following pairs would be more soluble in water? Explain.
c. butanal or hexanal
Write the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of each of the following compounds:
b. 3-hexanol
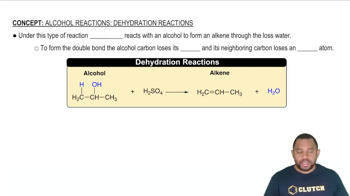
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula for the alkene produced by each of the following dehydration reactions:
b.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula for the aldehyde or ketone formed when each of the following alcohols is oxidized [O] (if no reaction, write none):
d.
Draw the condensed structural formulas for the aldehyde and carboxylic acid produced when each of the following is oxidized:
c. 3-chloro-1-propanol
Draw the condensed structural formula for the alcohol formed when each of the following is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst:
a. butyraldehyde