Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following:
a. trans-1-bromo-2-chloroethene

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Problem 33b
Problem 33b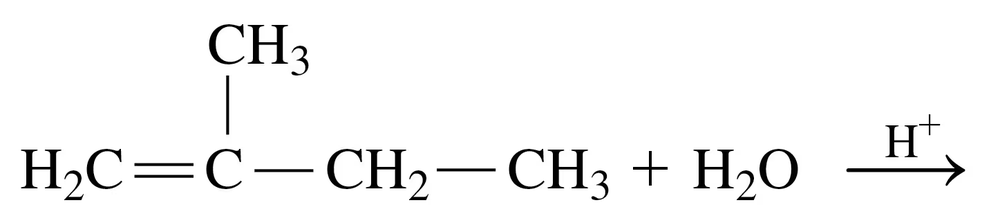
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following:
a. trans-1-bromo-2-chloroethene
Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following:
a. cis-1,2-difluoroethene
Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following:
b. trans-2-pentene
Draw the structural formula for the product in each of the following reactions:
a.
Draw the structural formula for the product in each of the following reactions:
b.