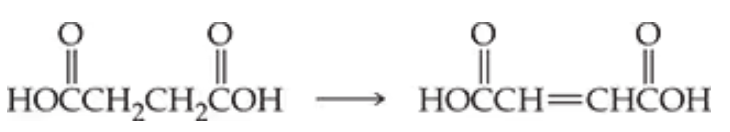Back
BackProblem 38a
Name an enzyme that acts on each molecule.
a. Amylose
Problem 38c
Name an enzyme that acts on each molecule.
c. DNA
Problem 39a
Name an enzyme that acts on each molecule.
a. Lactose
Problem 39c
Name an enzyme that acts on each molecule.
c. RNA
Problem 42c
What classes of enzymes would you expect to catalyze the following reactions?
c.
Problem 44b
What kind of reaction does each of these enzymes catalyze?
b. A transmethylase
Problem 44c
What kind of reaction does each of these enzymes catalyze?
c. A reductase
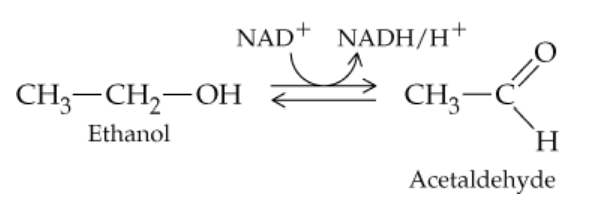
Problem 47
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) catalyzes the following reaction. To what class of enzymes does ADH belong?
Problem 48
What is the difference between the lock-and-key model of enzyme action and the induced-fit model?
Problem 49
Why is the induced-fit model a more likely model than the lock-and-key model?
Problem 52
How do you explain the observation that pepsin, a digestive enzyme found in the stomach, has a high catalytic activity at pH 1.5, while trypsin, an enzyme of the small intestine, has no activity at pH 1.5?
Problem 56a
What general effects would you expect the following changes to have on the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction for an enzyme that has its maximum activity at body temperature (about 37°C)?
a. Raising the temperature from 37°C to 70°C
Problem 56c
What general effects would you expect the following changes to have on the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction for an enzyme that has its maximum activity at body temperature (about 37°C)?
c. Adding an organic solvent, such as methanol
Problem 57c
What general effects would you expect the following changes to have on the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction for an enzyme that has its maximum activity at body temperature (about 37°C)?
c. Adding an oxidizing agent, such as hydrogen peroxide
Problem 58b
The text discusses three forms of enzyme inhibition: uncompetitive inhibition, competitive inhibition, and irreversible inhibition.
b. What kinds of bonds are formed between an enzyme and each of these three kinds of inhibitors?
Problem 59a
What kind of inhibition (uncompetitive, competitive, or irreversible) is present in each of the following:
a. Penicillin is used to treat certain bacterial infections. Penicillin is effective because it binds to the enzyme glycopeptide transpeptidase and does not dissociate.
Problem 59c
What kind of inhibition (uncompetitive, competitive, or irreversible) is present in each of the following:
c. The antibiotic deoxycycline inhibits the bacterial enzyme collagenase, slowing bacterial growth. Deoxycycline does not fit into the active site of collagenase and binds elsewhere on the enzyme.
Problem 63
One mechanism by which lead exerts its poisonous effect on enzymes can be stopped by chelation therapy with EDTA. Describe this type of lead poisoning and explain why it is reversible.
Problem 64
The meat tenderizer used in cooking is primarily papain, a protease enzyme isolated from the fruit of the papaya tree. Why do you suppose papain is so effective at tenderizing meat?
Problem 66
Why do allosteric enzymes have two types of binding sites?
Problem 69
What are the cellular advantages to feedback inhibition?
Problem 71
Activation of a zymogen is by covalent modification. How might phosphorylation or dephosphorylation (also covalent modification) modify an enzyme to make it more active (or more inactive)?
Problem 74
What criteria make a compound a vitamin?
Problem 75
What is the relationship between vitamins and enzymes?
Problem 76
Why is daily ingestion of vitamin C more critical than daily ingestion of vitamin A?
Problem 78
Why is it important that the macronutrients calcium and phosphorus be ingested in approximately equal amounts?
Problem 80
Look up the structures of vitamin C and vitamin E on the Web, and identify the functional groups in these vitamins.
Problem 81
What is the relationship between vitamin A and β-carotene?
Problem 83
How can you distinguish between a competitive inhibitor and an uncompetitive inhibitor experimentally?
Problem 84
What is the activation energy for a reaction? Why is activation energy necessary?