Identify and describe the evolutionary forces that can cause allele frequencies to change from one generation to the next.
Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels

Sanders3rd EditionGenetic Analysis: An Integrated ApproachISBN: 9780135564172Not the one you use?Change textbook
All textbooks Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels
Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels Problem 4
Problem 4
 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels
Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels Problem 4
Problem 4Chapter 20, Problem 4
Describe how natural selection can produce balanced polymorphism of allele frequencies through selection that favors heterozygotes.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of balanced polymorphism, which occurs when two or more alleles are maintained in a population's gene pool at stable frequencies over time.
Recognize that heterozygote advantage (also called overdominance) is a form of natural selection where individuals with heterozygous genotypes have higher fitness than either homozygous genotype.
Set up the fitness values for the three genotypes: let the fitness of homozygote AA be , heterozygote Aa be , and homozygote aa be , with and .
Use the concept that selection will increase the frequency of the heterozygote-favored allele combinations, but because both alleles contribute to heterozygotes, neither allele is lost, leading to a stable equilibrium of allele frequencies.
Explain that the equilibrium frequencies can be calculated by setting the change in allele frequency to zero and solving the equations derived from the relative fitness values, showing how natural selection maintains both alleles in the population.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the process where individuals with traits better suited to their environment have higher survival and reproductive success. Over time, this leads to changes in allele frequencies within a population, favoring alleles that confer a fitness advantage.
Recommended video:
Guided course
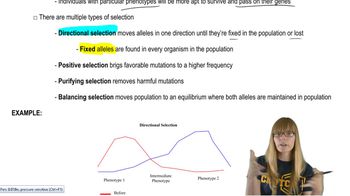
Natural Selection
Balanced Polymorphism
Balanced polymorphism occurs when two or more alleles are maintained in a population at stable frequencies due to selective advantages. This genetic diversity persists because heterozygotes have higher fitness than either homozygote, preventing any single allele from becoming fixed or lost.
Recommended video:
Guided course
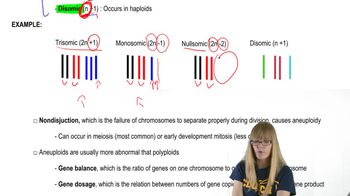
Aneuploidy
Heterozygote Advantage
Heterozygote advantage is a form of selection where individuals with two different alleles (heterozygotes) have greater fitness than those with two identical alleles (homozygotes). This advantage maintains multiple alleles in the gene pool, as seen in cases like sickle cell trait providing malaria resistance.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Hardy Weinberg
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
What insights have analyses of human mitochondrial DNA provided into our recent evolutionary past?
Textbook Question
What lines of evidence support the hypothesis that modern humans evolved in Africa and then subsequently migrated throughout the globe?
Textbook Question
Discuss how both gains and losses of regulatory elements may lead to human-specific traits.
Textbook Question
Thinking creatively about evolutionary mechanisms, identify at least two schemes that could generate allelic polymorphism in a population. Do not include the processes described in the answer to Problem 4.
3
views
Textbook Question
How do copy-number variants arise? Do they account for more polymorphism than SNPs within the human population?