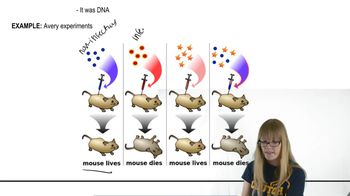
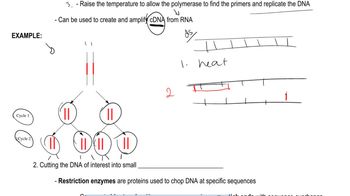
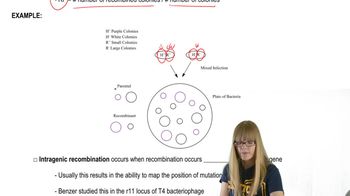
In the course of the Drosophila melanogaster genome project, the following genomic DNA sequences were obtained. Try to assemble the sequences into a single contig.
5' TTCCAGAACCGGCGAATGAAGCTGAAGAAG 3'
5' GAGCGGCAGATCAAGATCTGGTTCCAGAAC 3'
5' TGATCTGCCGCTCCGTCAGGCATAGCGCGT 3'
5' GGAGAATCGAGATGGCGCACGCGCTATGCC 3'
5' GGAGAATCGAGATGGCGCACGCGCTATGCC 3'
5' CCATCTCGATTCTCCGTCTGCGGGTCAGAT 3'
Go to the URL provided in Problem 14, and using the sequence you have just assembled, perform a blastn search in the 'Nucleotide collection (nr/nt)' database. Does the search produce sequences similar to your assembled sequence, and if so, what are they? Can you tell if your sequence is transcribed, and if it represents protein-coding sequence? Perform a tblastx search, first choosing the 'Nucleotide collection (nr/nt)' database and then limiting the search to human sequences by typing Homo sapiens in the organism box. Are homologous sequences found in the human genome? Annotate the assembled sequence.