The CAP binding site in the lac promoter is the location of positive regulation of gene expression for the operon. Identify what binds at this site to produce positive regulation, under what circumstances binding occurs, and how binding exerts a positive effect.
Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage

Sanders3rd EditionGenetic Analysis: An Integrated ApproachISBN: 9780135564172Not the one you use?Change textbook
All textbooks Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage
Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage Problem 7
Problem 7
 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage
Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage Problem 7
Problem 7Chapter 12, Problem 7
The trpL region contains four repeated DNA sequences that lead to the formation of stem-loop structures in mRNA. What are these stem-loop structures, and how do they affect transcription of the structural genes of the trp operon?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the trp operon: The trp operon in bacteria is a group of genes involved in the biosynthesis of tryptophan. It is regulated by transcriptional attenuation, which involves the trpL region.
Identify the trpL region: The trpL region is a leader sequence located upstream of the structural genes. It contains four repeated DNA sequences (regions 1, 2, 3, and 4) that can form stem-loop structures in the mRNA transcript.
Explain the stem-loop structures: The stem-loop structures are formed by complementary base pairing between these regions. Specifically, regions 1 and 2 can pair, regions 2 and 3 can pair, and regions 3 and 4 can pair. The pairing of regions 3 and 4 forms a terminator stem-loop, which halts transcription.
Describe the role of tryptophan levels: When tryptophan levels are high, the ribosome quickly translates the leader peptide encoded by the trpL region, allowing regions 3 and 4 to pair and form the terminator stem-loop. This stops transcription of the structural genes.
Explain the alternative pairing: When tryptophan levels are low, the ribosome stalls at the trp codons in region 1, allowing regions 2 and 3 to pair instead. This prevents the formation of the terminator stem-loop, allowing transcription of the structural genes to proceed.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stem-Loop Structures
Stem-loop structures are secondary RNA structures formed when a single strand of RNA folds back on itself, creating a double-stranded 'stem' and a loop. These structures play a crucial role in the regulation of gene expression, particularly in prokaryotes, by influencing the stability of mRNA and its interaction with ribosomes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ribosome Structure
trp Operon
The trp operon is a group of genes in bacteria that are involved in the biosynthesis of the amino acid tryptophan. It is regulated by a feedback mechanism where the presence of tryptophan inhibits the transcription of the operon, allowing the cell to conserve resources when tryptophan is abundant.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Trp Attenuation
Transcription Termination
Transcription termination is the process by which RNA polymerase stops synthesizing RNA and detaches from the DNA template. In the trp operon, the formation of stem-loop structures in the mRNA can signal RNA polymerase to terminate transcription prematurely, thereby preventing the synthesis of downstream structural genes when tryptophan levels are sufficient.
Recommended video:
Guided course
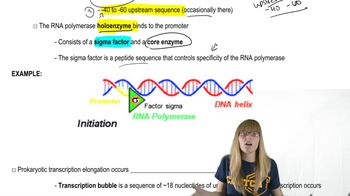
Prokaryotic Transcription
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Identify similarities and differences between an inducible operon and a repressible operon in terms of
The organization of structural genes of the operon.
Textbook Question
The transcription of -galactosidase and permease is inducible in lac⁺ bacteria with a wild-type lac operon. Explain the mechanism by which lactose gains access to the cell to induce transcription of the genes.
Textbook Question
Is attenuation the product of an allosteric effect? Is attenuation the result of a transcriptional or a translational activity? Explain your answers.
Textbook Question
What role does cAMP play in transcription of lac operon genes? What role does CAP play in transcription of lac operon genes?
Textbook Question
How would a cap⁻ mutation that produces an inactive CAP protein affect transcriptional control of the lac operon?