UV irradiation causes damage to bacterial DNA. What kind of damage is frequently caused and how does photolyase repair the damage?

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination
Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination Problem 6a
Problem 6aUltraviolet (UV) radiation is mutagenic.
What kind of DNA lesion does UV energy cause?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
DNA Lesions

Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
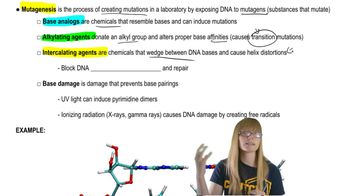
DNA Repair Mechanisms

In March 2011 an earthquake measuring approximately 9.0 on the Richter scale struck Fukushima, Japan. Several nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Daichii Nuclear Power Plant were damaged, and nuclear core meltdown occurred. A massive release of radiation accompanied damage to the plant, and 5 years later the incidence of thyroid cancer in children exposed to the radiation was determined to be well over 100 times more frequent than expected without radiation exposure. DNA damage and mutations resulting from radiation exposure are suspected of causing this increased cancer rate. What gene discussed in this chapter might be responsible for pausing the cell cycle of dividing cells long enough for radiation-induced damage to be repaired in cells?
In March 2011 an earthquake measuring approximately 9.0 on the Richter scale struck Fukushima, Japan. Several nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Daichii Nuclear Power Plant were damaged, and nuclear core meltdown occurred. A massive release of radiation accompanied damage to the plant, and 5 years later the incidence of thyroid cancer in children exposed to the radiation was determined to be well over 100 times more frequent than expected without radiation exposure. DNA damage and mutations resulting from radiation exposure are suspected of causing this increased cancer rate. Do you think it is possible that significant increases in the incidence of other types of cancer will occur in the future among people who were exposed to the Fukushima radiation? Why?
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is mutagenic.
How do UV-induced DNA lesions lead to mutation?
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is mutagenic.
Identify and describe two DNA repair mechanisms that remove UV-induced DNA lesions.
Researchers interested in studying mutation and mutation repair often induce mutations with various agents. What kinds of gene mutations are induced by
Chemical mutagens? Give two examples.