 Back
Back- Locate sulfur, selenium, chlorine, and bromine in the periodic table: (a) Which binary acid 1H2S, H2Se, HCl, or HBr2 is the strongest? Which is the weakest? Explain.
Problem 40
Problem 41
Which of the following pictures represents a solution of a weak diprotic acid, H2A? (Water molecules have been omitted for clarity.) Which pictures represent an impossible situation? Explain.

(a) (b) (c) (d)
Problem 43a
The following pictures represent solutions of three salts NaA (A- = X-, Y-, or Z-); water molecules and Na+ ions have been omitted for clarity.
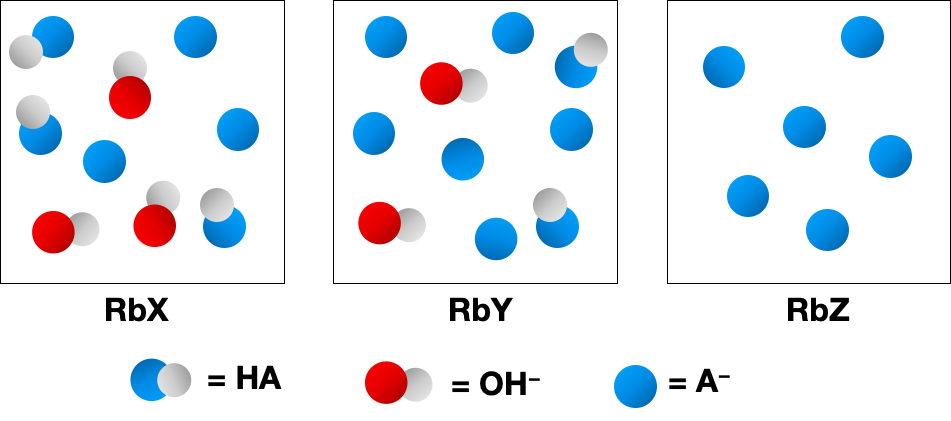
(a) Arrange the three A- anions in order of increasing base strength.
Problem 43b
The following pictures represent solutions of three salts NaA (A- = X-, Y-, or Z-); water molecules and Na+ ions have been omitted for clarity.

(b) Which A- anion has the strongest conjugate acid?
Problem 43c
The following pictures represent solutions of three salts NaA (A- = X-, Y-, or Z-); water molecules and Na+ ions have been omitted for clarity.

(c) Which A- anion has the smallest value of pKb?
Problem 44a
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3.

(a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction of M1H2O26 n + with water and write the equilibrium equation for the reaction.
Problem 44b
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3.
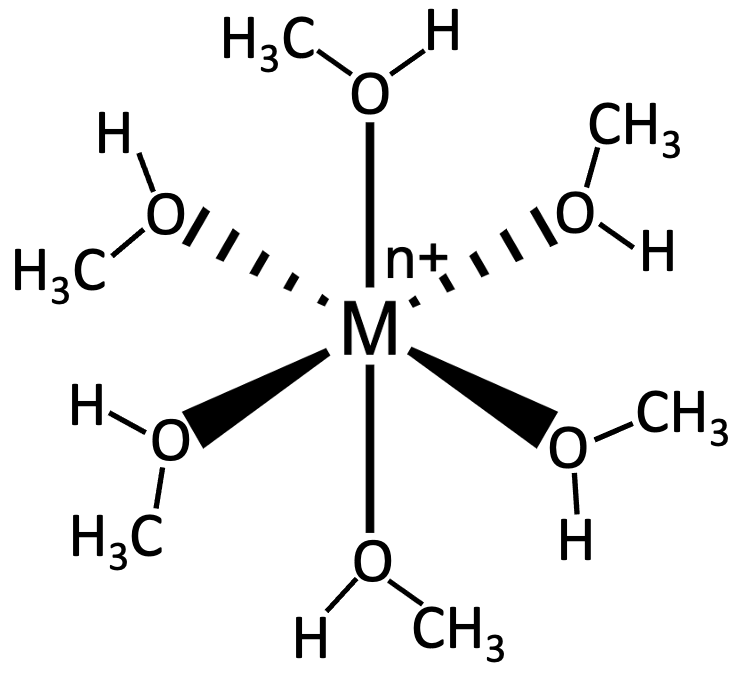
(b) Does the equilibrium constant increase, decrease, or remain the same as the value of n increases? Explain.
Problem 44c
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3. (c) Which M1H2O26n + ion 1n = 1,2, or 32 is the strongest acid, and which has the strongest conjugate base?
- Look at the electron-dot structures of the following molecules and ions: (b) Which can behave as a Lewis acid? Which can behave as a Lewis base?
Problem 45
- Which of the following are Brønsted–Lowry bases but not Arrhenius bases? (a) NH3 (b) HCO3-
Problem 48
- Which of the following can behave both as a Brønsted–Lowry acid and as a Brønsted–Lowry base? (a) HCO3- (b) CN- (c) H2O (d) H2CO3
Problem 49
- Aqueous solutions of hydrogen sulfide contain H2S, HS-, S2-, H3O+ , OH-, and H2O in varying concentrations. Which of these species can act only as an acid? Which can act only as a base? Which can act both as an acid and as a base?
Problem 54
- The hydronium ion H3O+ is the strongest acid that can exist in aqueous solution because stronger acids dissociate by transferring a proton to water. What is the strongest base that can exist in aqueous solution?
Problem 55
- Choose from the conjugate acid–base pairs HSO4- >SO42-, HF>F-, and NH4+>NH3 to complete the following equation with the pair that gives an equilibrium constant Kc 7 1. _____ + NO2 - S _____ + HNO2
Problem 56
- Choose from the conjugate acid–base pairs F- > HF, NH3 > NH4+, and NO3- > HNO3, to complete the following equation with the pair that gives an equilibrium constant Kc > 1. _____ + H2CO3 ⇌ _____ + HCO3-
Problem 57
- Which acid in each of the following pairs has the stronger conjugate base? See Table 16.1 to compare the relative strengths of conjugate acid-base pairs. (a) HCl or HF
Problem 58
- Which base in each of the following pairs has the stronger conjugate acid? See Table 16.1 to compare the relative strengths of conjugate acid-base pairs. (a) Cl- or CO32-
Problem 59
Problem 60a
Arrange each group of compounds in order of increasing acid strength. Explain your reasoning. (a) HCl, H2S, PH3
- Calculate the percent dissociation of 0.10 M hydrazoic acid (HN3, Ka = 1.9 X 10^-5). Recalculate the percent dissociation of 0.10 M HN3 in the presence of 0.10 M HCl, and explain the change.
Problem 61
- Calculate the pH of 100.0 mL of 0.30 M NH3 before and after the addition of 4.0 g of NH4NO3, and account for the change. Assume that the volume remains constant.
Problem 62
Problem 63a
Identify the weakest acid in each of the following sets. Explain your reasoning. (a) H2SO3, HClO3, HClO4
Problem 63b
Identify the weakest acid in each of the following sets. Explain your reasoning. (b) NH3, H2O, H2S
Problem 63c
Identify the weakest acid in each of the following sets. Explain your reasoning. (c) B(OH)3, Al(OH)3, Ga(OH)3
- Identify the stronger acid in each of the following pairs. Explain your reasoning. (b) H3PO4 or H3AsO4
Problem 64
Problem 65a,b
Identify the stronger base in each of the following pairs.
Explain your reasoning.
(a) ClO2- or ClO3-
(b) HSO4- or HSeO4-
Problem 65c
Identify the stronger base in each of the following pairs.
Explain your reasoning.
(c) HS- or OH-
Problem 65d
Identify the stronger base in each of the following pairs.
Explain your reasoning.
(d) HS- or Br-
- Water at 500 °C and 250 atm is a supercritical fluid. Under these conditions, Kw is approximately 1.7 * 10^-19. Estimate [H3O+] and [OH-] at 500 °C. Is the water acidic, basic, or neutral?
Problem 73
Problem 76d
Calculate the H3O+ concentration to the correct number of significant figures for solutions with the following pH values. (d) 14.25
Problem 76e
Calculate the H3O+ concentration to the correct number of significant figures for solutions with the following pH values. (e) -1.0
