Textbook Question
Identify the weakest acid in each of the following sets. Explain your reasoning. (b) NH3, H2O, H2S

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

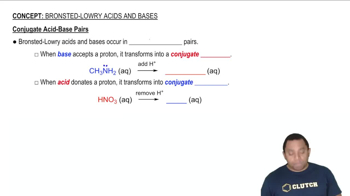

Identify the weakest acid in each of the following sets. Explain your reasoning. (b) NH3, H2O, H2S
Identify the weakest acid in each of the following sets. Explain your reasoning. (c) B(OH)3, Al(OH)3, Ga(OH)3
Identify the stronger base in each of the following pairs.
Explain your reasoning.
(c) HS- or OH-
Identify the stronger base in each of the following pairs.
Explain your reasoning.
(d) HS- or Br-