Textbook Question
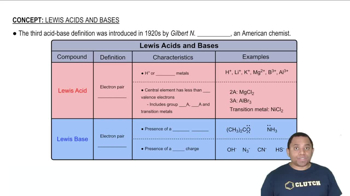
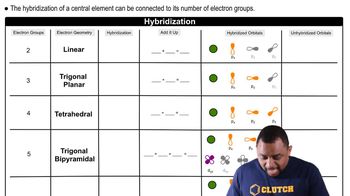
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3.
(a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction of M1H2O26 n + with water and write the equilibrium equation for the reaction.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3.
(a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction of M1H2O26 n + with water and write the equilibrium equation for the reaction.
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3.
(b) Does the equilibrium constant increase, decrease, or remain the same as the value of n increases? Explain.
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3. (c) Which M1H2O26n + ion 1n = 1,2, or 32 is the strongest acid, and which has the strongest conjugate base?