Ephedrine, a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. This compound is a weak organic base: C10H15ON1aq2 + H2O1l2 Δ C10H15ONH+1aq2 + OH-1aq2 A 0.035 M solution of ephedrine has a pH of 11.33. (a) What are the equilibrium concentrations of C10H15ON, C10H15ONH+, and OH-?

Phenol, C6H5OH, has a Ka of 1.3 * 10^-10. (c) Is phenol a stronger or weaker acid than water?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
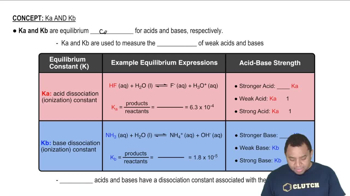
Comparative Acidity
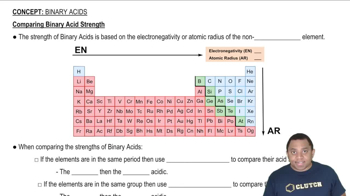
Proton Donation
Ephedrine, a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. This compound is a weak organic base: C10H15ON1aq2 + H2O1l2 Δ C10H15ONH+1aq2 + OH-1aq2 A 0.035 M solution of ephedrine has a pH of 11.33. (b) Calculate Kb for ephedrine.
Codeine 1C18H21NO32 is a weak organic base. A 5.0 * 10-3M solution of codeine has a pH of 9.95. Calculate the value of Kb for this substance. What is the pKb for this base?
Use the acid-dissociation constants in Table 16.3 to arrange these oxyanions from strongest base to weakest: SO42-, CO32-, SO32-, and PO43-.
Given that Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 * 10-5 and that for hypochlorous acid is 3.0 * 10-8, which is the stronger acid?
Which is the stronger base, the acetate ion or the hypochlorite ion?
