Textbook Question
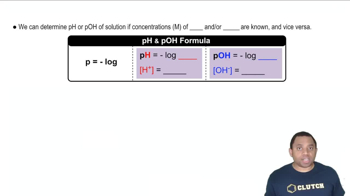
Ephedrine, a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. This compound is a weak organic base: C10H15ON1aq2 + H2O1l2 Δ C10H15ONH+1aq2 + OH-1aq2 A 0.035 M solution of ephedrine has a pH of 11.33. (a) What are the equilibrium concentrations of C10H15ON, C10H15ONH+, and OH-?