Ephedrine, a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. This compound is a weak organic base: C10H15ON1aq2 + H2O1l2 Δ C10H15ONH+1aq2 + OH-1aq2 A 0.035 M solution of ephedrine has a pH of 11.33. (a) What are the equilibrium concentrations of C10H15ON, C10H15ONH+, and OH-?
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 16, Problem 74
Codeine 1C18H21NO32 is a weak organic base. A 5.0 * 10-3M solution of codeine has a pH of 9.95. Calculate the value of Kb for this substance. What is the pKb for this base?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the relationship between pH and pOH. Since pH + pOH = 14, calculate the pOH of the solution using the given pH value: \( \text{pOH} = 14 - \text{pH} \).
Step 2: Calculate the hydroxide ion concentration \([OH^-]\) from the pOH using the formula \([OH^-] = 10^{-\text{pOH}}\).
Step 3: Write the expression for the base dissociation constant \(K_b\) for codeine. The general expression is \(K_b = \frac{[BH^+][OH^-]}{[B]}\), where \([B]\) is the initial concentration of the base, and \([BH^+]\) and \([OH^-]\) are the concentrations of the products at equilibrium.
Step 4: Assume that the change in concentration of codeine \([B]\) is negligible compared to its initial concentration. Therefore, \([B] \approx 5.0 \times 10^{-3} M\). Use the \([OH^-]\) calculated in Step 2 to find \(K_b\).
Step 5: Calculate the \(pK_b\) using the formula \(pK_b = -\log(K_b)\). This will give you the pKb value for codeine.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Weak Bases and pH
Weak bases are substances that partially ionize in solution, leading to a less than complete dissociation of hydroxide ions. The pH of a solution indicates its acidity or basicity, with values above 7 signifying basic conditions. In this case, the pH of 9.95 suggests that the solution is basic, which is characteristic of a weak base like codeine.
Recommended video:
Guided course
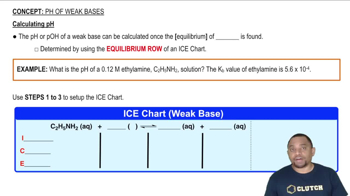
Calculating pH of Weak Bases Example
Equilibrium Constant (Kb)
The base dissociation constant (Kb) quantifies the strength of a weak base in solution. It is defined as the equilibrium constant for the reaction where the base accepts a proton from water, forming hydroxide ions. The Kb value can be calculated using the concentrations of the products and reactants at equilibrium, which is essential for determining the basicity of codeine.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Equilibrium Constant K
Relationship between Kb and pKb
The pKb is the negative logarithm of the base dissociation constant (Kb) and provides a convenient way to express the strength of a base. A lower pKb value indicates a stronger base. The relationship is given by the formula pKb = -log(Kb), allowing for easy conversion between the two measures, which is crucial for understanding the basicity of codeine in this context.
Recommended video:
Guided course
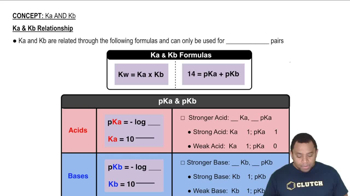
Ka and Kb Relationship
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Ephedrine, a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. This compound is a weak organic base: C10H15ON1aq2 + H2O1l2 Δ C10H15ONH+1aq2 + OH-1aq2 A 0.035 M solution of ephedrine has a pH of 11.33. (b) Calculate Kb for ephedrine.
Textbook Question
Use the acid-dissociation constants in Table 16.3 to arrange these oxyanions from strongest base to weakest: SO42-, CO32-, SO32-, and PO43-.
Textbook Question
Given that Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 * 10-5 and that for hypochlorous acid is 3.0 * 10-8, which is the stronger acid?
