Textbook Question
Use the acid-dissociation constants in Table 16.3 to arrange these oxyanions from strongest base to weakest: SO42-, CO32-, SO32-, and PO43-.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

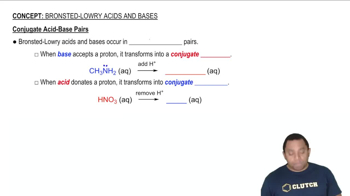
Use the acid-dissociation constants in Table 16.3 to arrange these oxyanions from strongest base to weakest: SO42-, CO32-, SO32-, and PO43-.
Given that Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 * 10-5 and that for hypochlorous acid is 3.0 * 10-8, which is the stronger acid?
Calculate Kb values for CH3COO- and ClO-.
Given that Kb for ammonia is 1.8 × 10-5 and that for hydroxylamine is 1.1 × 10-8, which is the stronger base?
Which is the stronger acid, the ammonium ion or the hydroxylammonium ion?