Back
BackProblem 13
Write each equation in its equivalent logarithmic form. ∛8 = 2
Problem 13
Graph each function by making a table of coordinates. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn graph. g(x) = (3/2)x
Problem 13
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 1–22 by expressing each side as a power of the same base and then equating exponents. 31-x=1/27
Problem 13
Use properties of logarithms to expand each logarithmic expression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. ln(e2/5)
- In Exercises 13–15, write each equation in its equivalent exponential form. 1/2 = log49 7
Problem 13
Problem 15
Use properties of logarithms to expand each logarithmic expression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. logb x3
Problem 15
Write each equation in its equivalent exponential form. log3 81 = y
Problem 15
Graph each function by making a table of coordinates. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn graph. h(x) = (1/2)x
Problem 15
Write each equation in its equivalent logarithmic form. 132 = x
Problem 15
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 1–22 by expressing each side as a power of the same base and then equating exponents. 6(x−3)/4=√6
Problem 17
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 1–22 by expressing each side as a power of the same base and then equating exponents. 4x=1/√2
Problem 17
Write each equation in its equivalent logarithmic form. b3 = 1000
Problem 17
Use properties of logarithms to expand each logarithmic expression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. log N-6
Problem 17
Graph each function by making a table of coordinates. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn graph. f(x) = (0.6)x
Problem 18
In Exercises 16–18, write each equation in its equivalent logarithmic form. 13^y = 874
Problem 19
Use properties of logarithms to expand each logarithmic expression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator.
Problem 19
Write each equation in its equivalent logarithmic form. 7y = 200
Problem 19
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 1–22 by expressing each side as a power of the same base and then equating exponents. 8(x+3)=16(x−1)
Problem 19
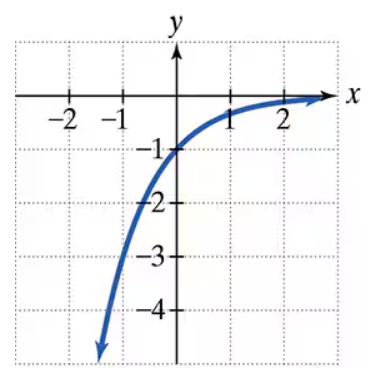
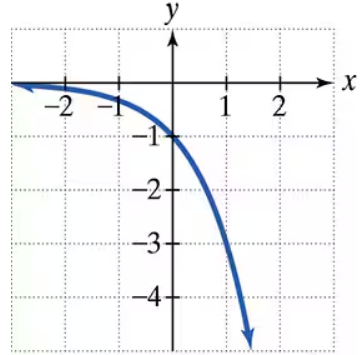
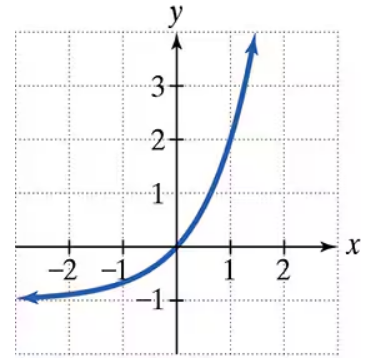
In Exercises 19–24, the graph of an exponential function is given. Select the function for each graph from the following options:
Problem 20
In Exercises 19–29, evaluate each expression without using a calculator. If evaluation is not possible, state the reason. log5 (1/5)
Problem 21
Evaluate each expression without using a calculator. log4 16
Problem 21
The graph of an exponential function is given. Select the function for each graph from the following options:
Problem 21
Use properties of logarithms to expand each logarithmic expression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. logb (x2 y)
Problem 21
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 1–22 by expressing each side as a power of the same base and then equating exponents. e(x+1)=1/e
Problem 22
In Exercises 19–29, evaluate each expression without using a calculator. If evaluation is not possible, state the reason. log16 4
Problem 23
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 23–48. Express the solution set in terms of natural logarithms or common logarithms. Then use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. 10x=3.91
Problem 23
Evaluate each expression without using a calculator. log2 64
Problem 23
The graph of an exponential function is given. Select the function for each graph from the following options:
Problem 23
Use properties of logarithms to expand each logarithmic expression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator.
Problem 24
Evaluate each expression without using a calculator. log3 27