Back
BackProblem 68
Use intercepts to graph each equation. 6x-9y-18 = 0
Problem 68
Begin by graphing the square root function, f(x) = √x. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = √x + 1
Problem 69
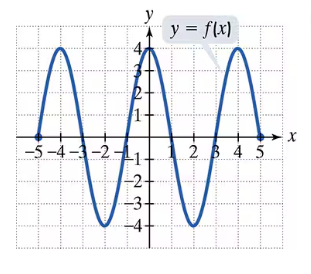
In Exercises 65–70, use the graph of f to find each indicated function value. f(-3)
Problem 69
Graph both equations in the same rectangular coordinate system and find all points of intersection. Then show that these ordered pairs satisfy the equations. (x − 2)²+(y+3)² = 4, y = x - 3
Problem 69
Find a. (fog) (x) b. the domain of f o g. f(x) = x/(x+1), g(x) = 4/x
Problem 69
In Exercises 67–69, begin by graphing the absolute value function, f(x) = |x|. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. r(x) = (1/2) |x + 2|
Problem 70
Begin by graphing the square root function, f(x) = √x. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = √(x+1)
Problem 71
Find a. (fog) (x) b. the domain of f o g.
f(x) = √x, g(x) = x − 2
Problem 71
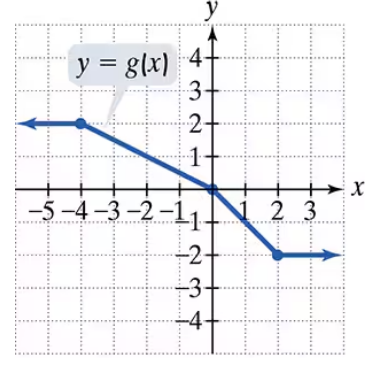
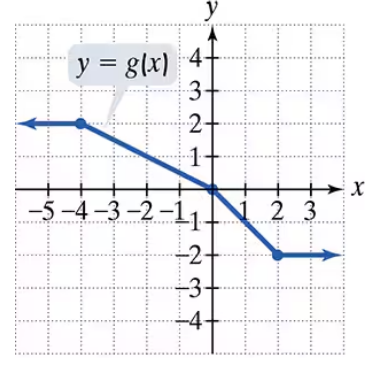
Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71–76.
Find g(-4)
Problem 72
Begin by graphing the square root function, f(x) = √x. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. h(x)=-√(x + 1)
Problem 72
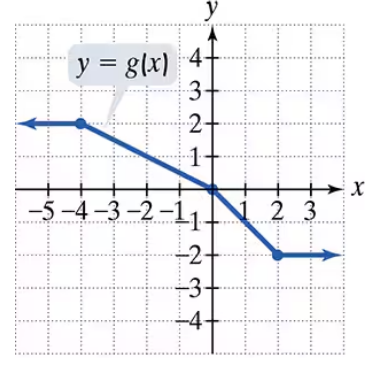
Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71–76.
Find g(2)
Problem 72a
Use intercepts to graph each equation. 6x-3y+15=0
Problem 73
Find a. (fog) (x) b. the domain of f o g.
f(x) = x² + 4, g(x) = √(1 − x)
Problem 74
Begin by graphing the square root function, f(x) = √x. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. h(x)=√(-x+1)
Problem 74
Find the slope of the line passing through each pair of points or state that the slope is undefined. Assume that all variables represent positive real numbers. Then indicate whether the line through the points rises, falls, is horizontal, or is vertical. (-a, 0) and (0, -b)
Problem 75
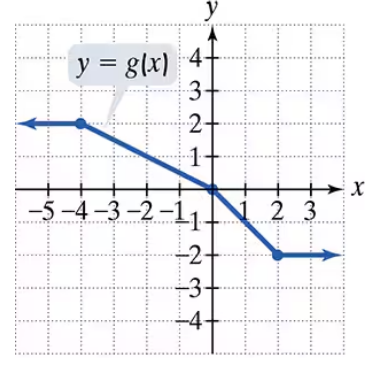
Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71–76.
For what value of x is g(x) = 1?
Problem 75
Express the given function h as a composition of two functions ƒ and g so that h(x) = (fog) (x).
h(x) = (3x − 1)4
Problem 76
Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71–76.
For what value of x is g(x) = -1?
Problem 76
Begin by graphing the square root function, f(x) = √x. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = 2√(x+1)
Problem 77
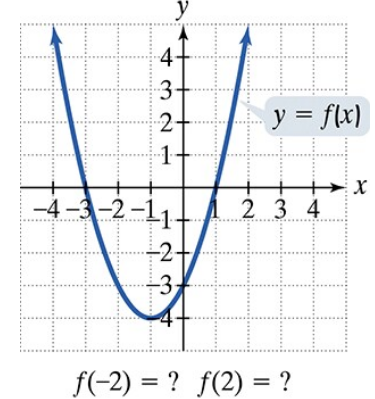
In Exercises 77–92, use the graph to determine a.the x-intercepts, if any; b. the y-intercept, if any; and e. the missing function values, indicated by question marks, below each graph.

Problem 77
Find the domain of each function. g(x) = 4/(x - 7)
Problem 77
Use the graph to determine a.the x-intercepts, if any; b. the y-intercept, if any; and e. the missing function values, indicated by question marks, below each graph.
Problem 77a
Express the given function h as a composition of two functions ƒ and g so that h(x) = (fog) (x). h(x) = ∛(x² – 9)
Problem 78
Begin by graphing the square root function, f(x) = √x. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. h(x) = √(x+1)-1
Problem 78
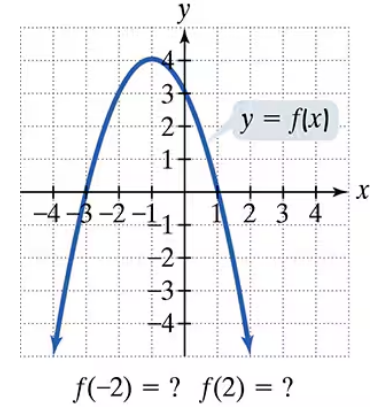
In Exercises 77–92, use the graph to determine a.the x-intercepts, if any; b. the y-intercept, if any; and e. the missing function values, indicated by question marks, below each graph.

Problem 78
Give the slope and y-intercept of each line whose equation is given. Assume that B ≠ 0. Ax = By - C
Problem 78
Use the graph to determine a.the x-intercepts, if any; b. the y-intercept, if any; and e. the missing function values, indicated by question marks, below each graph.
Problem 79
Find the domain of each function.
Problem 79
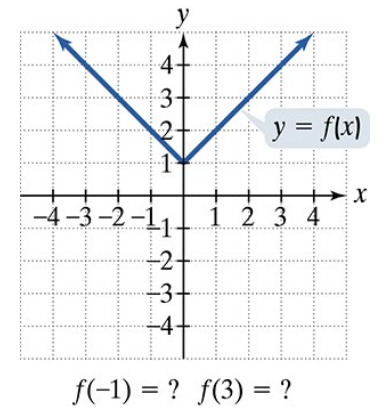
Use the graph to determine a.the x-intercepts, if any; b. the y-intercept, if any; and e. the missing function values, indicated by question marks, below each graph.
Problem 79
In Exercises 77–92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b. the function's range; and e. the missing function values, indicated by question marks, below each graph.