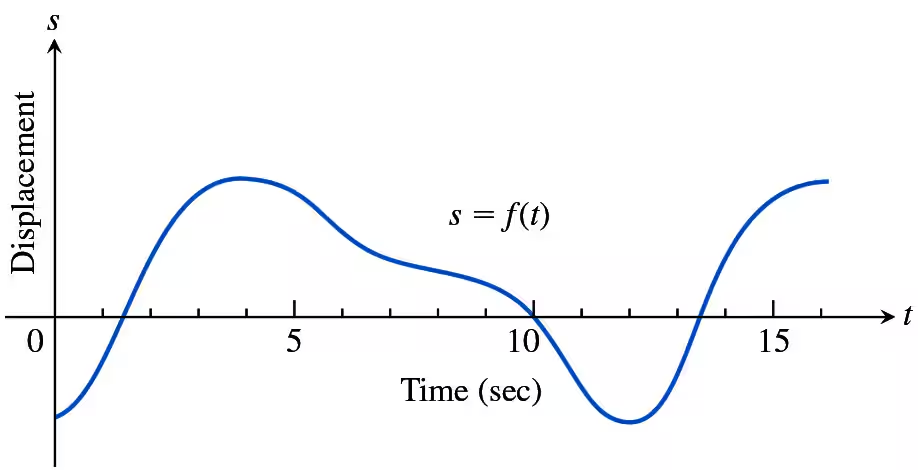
Understanding Motion from Graphs
The accompanying figure shows the velocity v = f(t) of a particle moving on a horizontal coordinate line.
c. When does the particle move at its greatest speed?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 6:29m
6:29mMaster Derivatives Applied To Velocity with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning