What is the difference between an epitope and an antigen?

What is one of the differences between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells?
a. CD4+ cells are immature, and CD8+ cells are mature.
b. CD4+ cells are activated, and CD8+ cells are not.
c. CD4+ cells interact with class II MHC proteins, and CD8+ cells interact with class I MHC proteins.
d. CD4+ cells activate cell-mediated responses, and CD8+ cells activate humoral responses.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
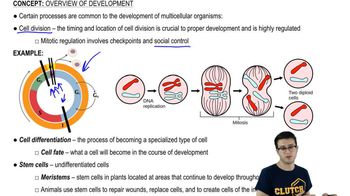
T Cell Differentiation
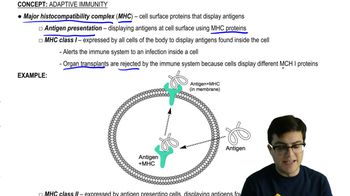
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
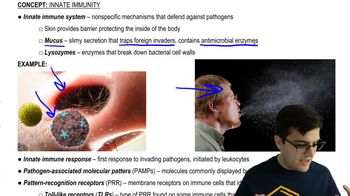
Immune Response Activation
What is the primary difference between the innate and adaptive immune responses?
a. The innate immune response does not distinguish between pathogens, while the adaptive immune response does.
b. Only the innate immune response is activated by antigens.
c. The adaptive immune response generates immunological memory and is more specific than the innate immune response.
d. The innate immune response does not kill cells; the adaptive immune response does.
The overall role of the inflammatory response is to
a. Contain and eliminate foreign cells and material at the site of infection.
b. Increase heat at the site of infection to activate enzymes used in the immune response.
c. Produce antibodies that bind to and eliminate invading cells.
d. Increase blood flow at the site of a wound to flush out invading pathogens.
Explain how gene recombination leads to the production of vast numbers of different B-cell receptors.
What steps are required for most B cells to become fully activated and differentiate into plasma cells?
Why is clonal selection necessary for the adaptive immune response but not the innate immune response? Select True or False for each statement.
T/F The adaptive immune response uses receptors to recognize pathogens, and the innate immune response does not.
T/F There is more receptor diversity in the adaptive immune response than in the innate immune response.
T/F Cells in the innate immune response do not require activation, and those in the adaptive immune response do.
T/F Clonal selection is used for targeting pathogens, and the innate immune response is used only to stop blood flow from the wound.
