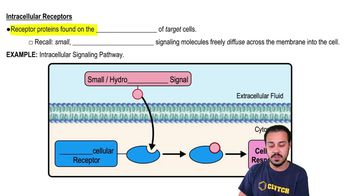
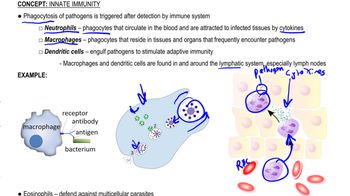
What is one of the differences between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells?
a. CD4+ cells are immature, and CD8+ cells are mature.
b. CD4+ cells are activated, and CD8+ cells are not.
c. CD4+ cells interact with class II MHC proteins, and CD8+ cells interact with class I MHC proteins.
d. CD4+ cells activate cell-mediated responses, and CD8+ cells activate humoral responses.