What is the difference between an epitope and an antigen?
Ch. 48 - The Immune System in Animals

Chapter 48, Problem 1
What is the primary difference between the innate and adaptive immune responses?
a. The innate immune response does not distinguish between pathogens, while the adaptive immune response does.
b. Only the innate immune response is activated by antigens.
c. The adaptive immune response generates immunological memory and is more specific than the innate immune response.
d. The innate immune response does not kill cells; the adaptive immune response does.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the innate immune response: It is the body's first line of defense against pathogens and is non-specific, meaning it does not distinguish between different types of pathogens. It includes physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes, as well as immune cells like phagocytes.
Understand the adaptive immune response: This response is specific to particular pathogens and involves the activation of lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). It is characterized by its ability to remember past infections, leading to a faster and more efficient response upon re-exposure to the same pathogen.
Compare the specificity of the two responses: The innate immune response is non-specific and acts the same way regardless of the pathogen, while the adaptive immune response is highly specific and tailored to the specific antigens present on the pathogen.
Consider the role of immunological memory: The adaptive immune response generates immunological memory, which allows the immune system to respond more rapidly and effectively to pathogens it has encountered before. The innate immune response does not have this capability.
Evaluate the options given in the problem: Based on the understanding of innate and adaptive immune responses, identify which option correctly describes the primary difference between them, focusing on specificity and memory.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Innate Immune Response
The innate immune response is the body's first line of defense against pathogens, characterized by its ability to respond quickly and non-specifically to a wide range of invaders. It includes physical barriers like skin, chemical barriers like stomach acid, and cellular defenses such as phagocytes. Unlike the adaptive immune response, it does not distinguish between different types of pathogens.
Recommended video:
Guided course
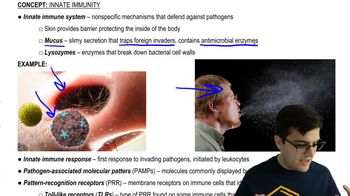
Innate Immune Response
Adaptive Immune Response
The adaptive immune response is a specialized defense mechanism that targets specific pathogens with precision. It involves the activation of lymphocytes, such as B cells and T cells, which recognize and remember specific antigens. This response is slower to develop but provides long-lasting protection through immunological memory, allowing the body to respond more effectively to future infections by the same pathogen.
Recommended video:
Guided course
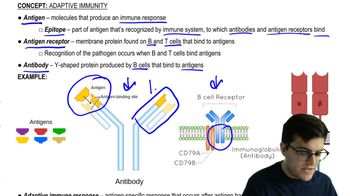
Adaptive Immune Response
Immunological Memory
Immunological memory is a hallmark of the adaptive immune response, enabling the immune system to remember and respond more efficiently to previously encountered pathogens. This memory is established after the initial exposure to an antigen, leading to a faster and more robust response upon subsequent exposures. It is the basis for the effectiveness of vaccines, which prime the immune system to recognize and combat specific pathogens.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Neuroplasticity, Learning, and Memory
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The overall role of the inflammatory response is to
a. Contain and eliminate foreign cells and material at the site of infection.
b. Increase heat at the site of infection to activate enzymes used in the immune response.
c. Produce antibodies that bind to and eliminate invading cells.
d. Increase blood flow at the site of a wound to flush out invading pathogens.
Textbook Question
What is one of the differences between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells?
a. CD4+ cells are immature, and CD8+ cells are mature.
b. CD4+ cells are activated, and CD8+ cells are not.
c. CD4+ cells interact with class II MHC proteins, and CD8+ cells interact with class I MHC proteins.
d. CD4+ cells activate cell-mediated responses, and CD8+ cells activate humoral responses.
