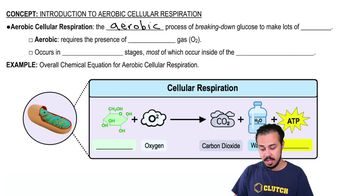
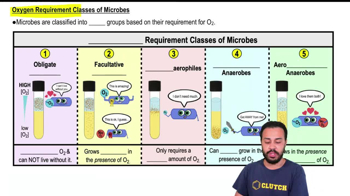
Evaluate these statements about Koch's postulates, which are used to establish a causative link between a specific microbe and a specific disease. Select True or False for each statement.
T/FThe microbe must be present in individuals suffering from the disease and absent from healthy individuals.
T/FThe microbe must be isolated and grown in pure culture.
T/FIf organisms from the pure culture are injected into a healthy experimental animal, the disease symptoms should appear.
T/FThe microbe does not have to be isolated from the experimental animal as long as the disease is present.