How does telomerase prevent linear chromosomes from shortening during replication?

What aspect of DNA structure makes it possible for the proteins of nucleotide excision repair to recognize many different types of DNA damage?
(c) the energy differences between correct and incorrect base pairs
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
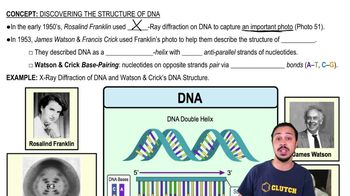
DNA Structure
Nucleotide Excision Repair

Base Pairing Energy Differences
What aspect of DNA structure makes it possible for the proteins of nucleotide excision repair to recognize many different types of DNA damage?
(a) the polarity of each DNA strand
What aspect of DNA structure makes it possible for the proteins of nucleotide excision repair to recognize many different types of DNA damage?
(b) the antiparallel orientation of strands in the double helix
What aspect of DNA structure makes it possible for the proteins of nucleotide excision repair to recognize many different types of DNA damage?
(d) the regularity of DNA's structure
In the late 1950s, Herbert Taylor grew bean root-tip cells in a solution of radioactive thymidine (a precursor to one of the deoxyribonucleotides in DNA) and allowed them to undergo one round of DNA replication. He then transferred the cells to a solution without radioactive thymidine, allowed them to replicate again, and examined their chromosomes for the presence of radioactivity. His results are shown in the following figure, where red indicates a radioactive chromatid.
(b) What would the results of Taylor's experiment be if eukaryotes used a conservative mode of DNA replication?
In the late 1950s, Herbert Taylor grew bean root-tip cells in a solution of radioactive thymidine (a precursor to one of the deoxyribonucleotides in DNA) and allowed them to undergo one round of DNA replication. He then transferred the cells to a solution without radioactive thymidine, allowed them to replicate again, and examined their chromosomes for the presence of radioactivity. His results are shown in the following figure, where red indicates a radioactive chromatid.
(a) Draw labeled diagrams of double-stranded DNA molecules that explain the pattern of radioactivity observed in the sister chromatids after the first and second rounds of replication.
