Back
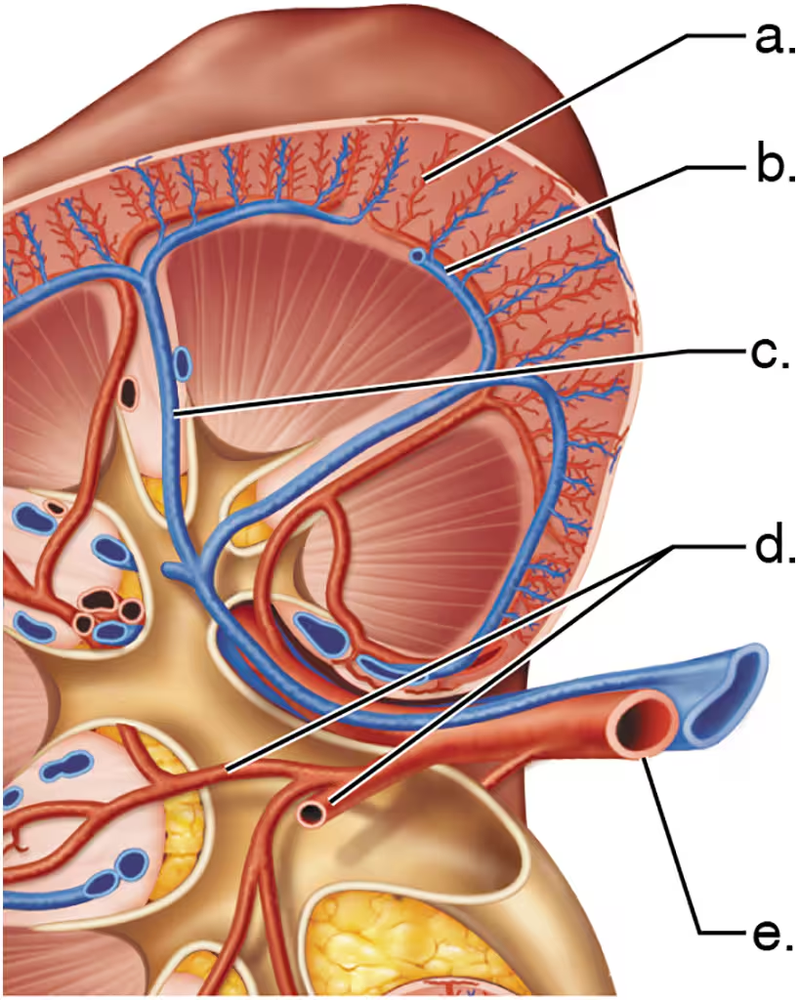
BackProblem 1a
More than one choice may apply.
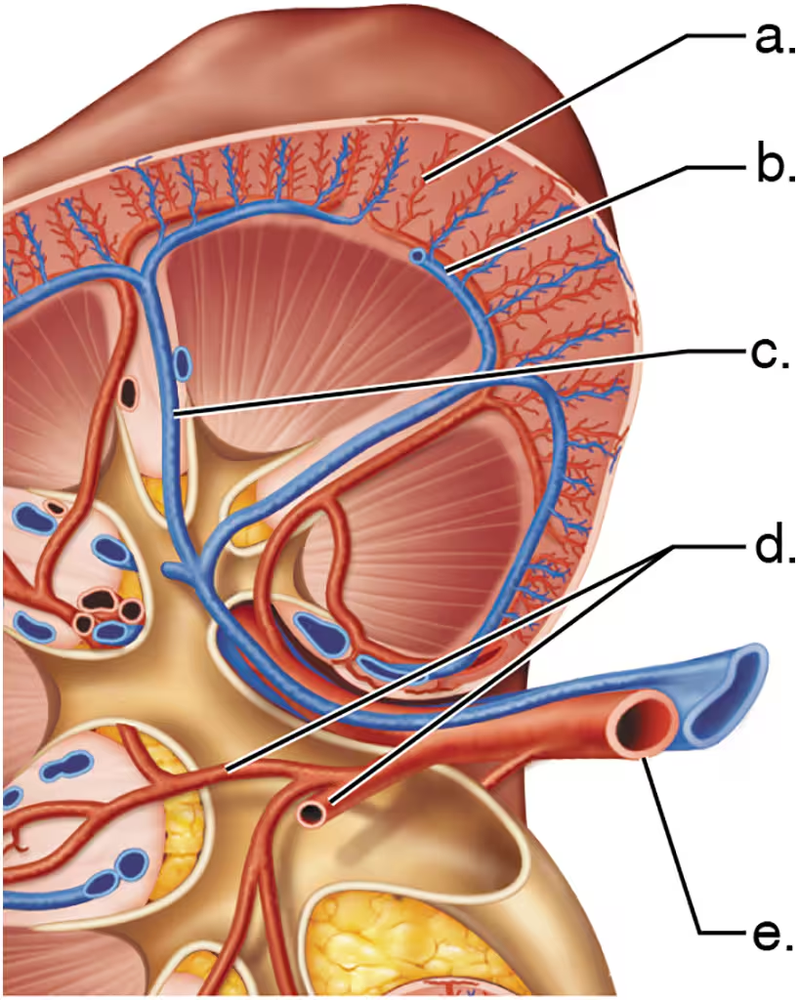
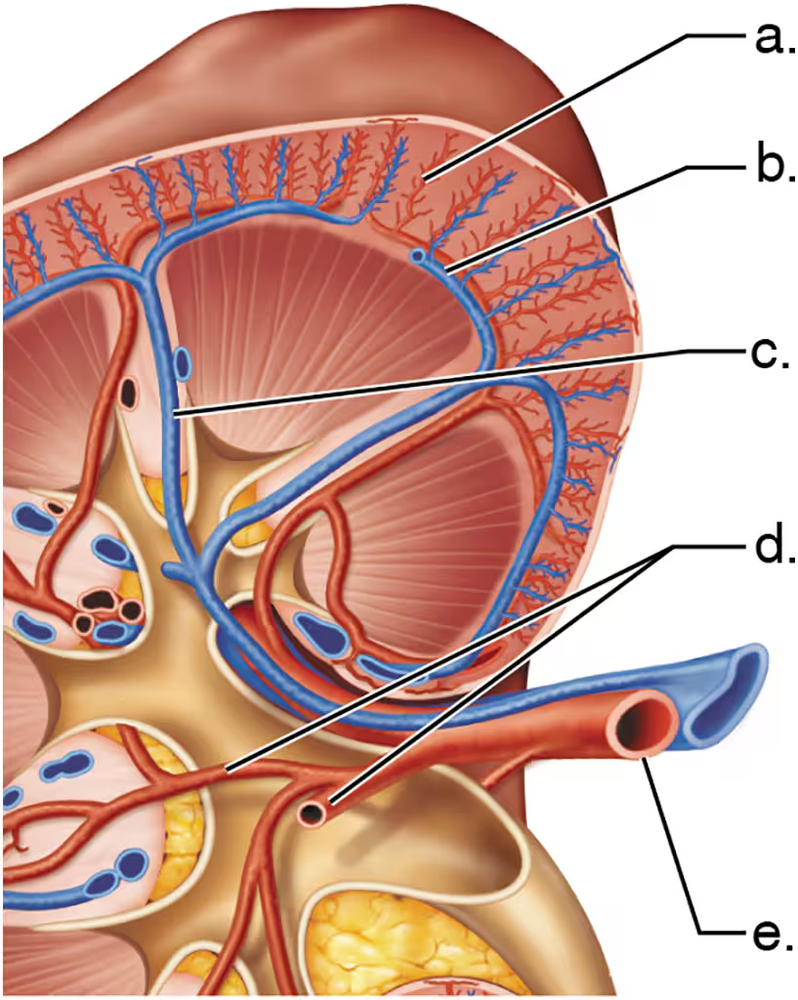
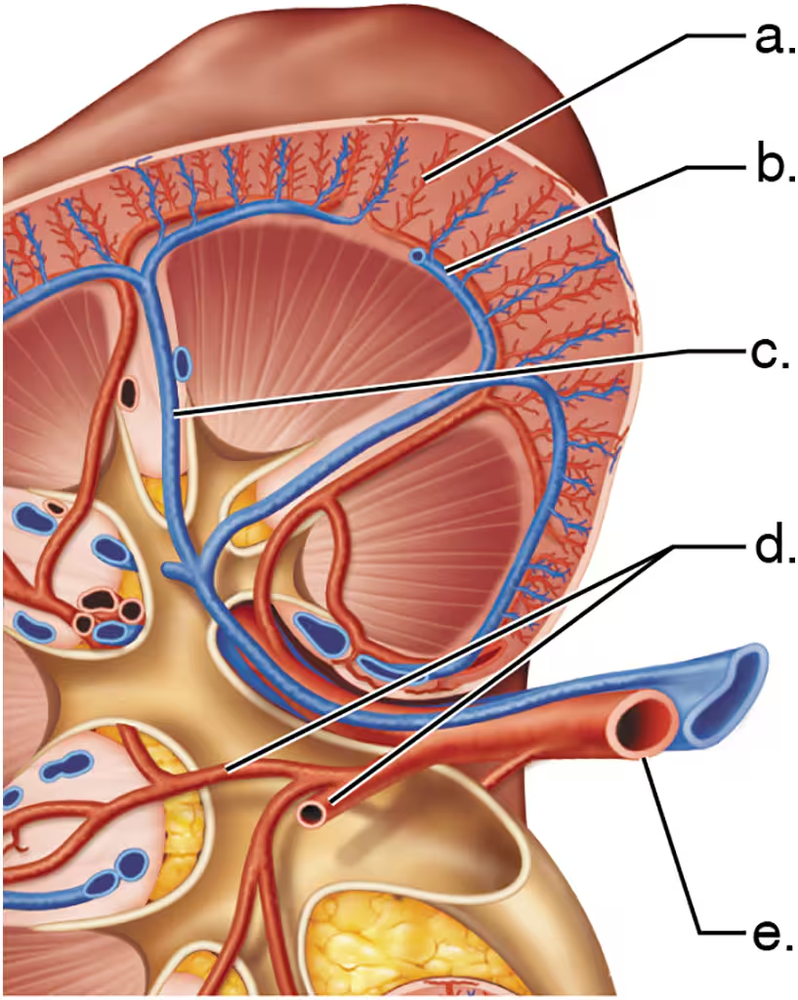
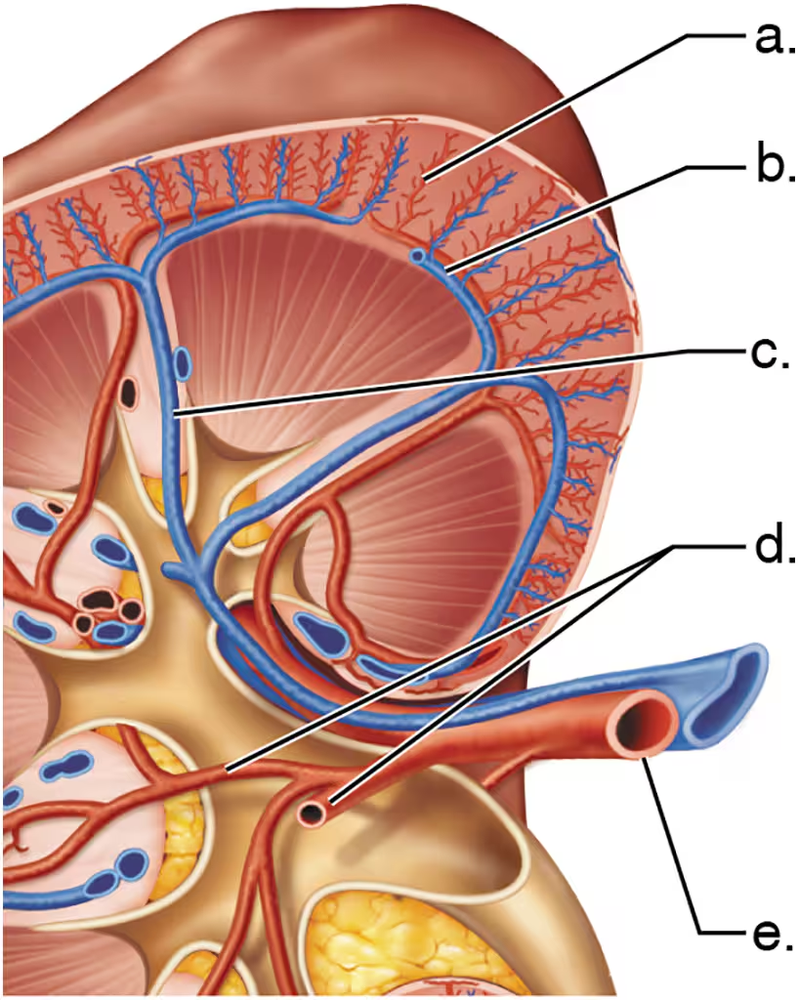
Match each letter from the figure with the correct blood vessel name.
Arcuate vein
Problem 1b
More than one choice may apply.
Match each letter from the figure with the correct blood vessel name.
Segmental arteries
Problem 1c
More than one choice may apply.
Match each letter from the figure with the correct blood vessel name.
Renal artery
Problem 1d
Match each letter from the figure with the correct blood vessel name.
Cortical radiate artery
Problem 1e
More than one choice may apply.
Match each letter from the figure with the correct blood vessel name.
Interlobar vein
Problem 2
More than one choice may apply.
What is the glomerulus?
a. The same as the renal tubule
b. The same as Bowman's capsule
c. The same as the nephron
d. Capillaries
Problem 3
More than one choice may apply.
Urine passes through the ureters by which mechanism?
a. Ciliary action
b. Gravity alone
c. Peristalsis
d. Suction
Problem 5
More than one choice may apply.
Which of the following is dependent on tubular secretion?
a. Clearing penicillin from the blood
b. Removal of nitrogenous wastes that have been reabsorbed
c. Removal of excess potassium ions from the blood
d. Control of blood pH
Problem 10
Describe the location of the kidneys in the body.
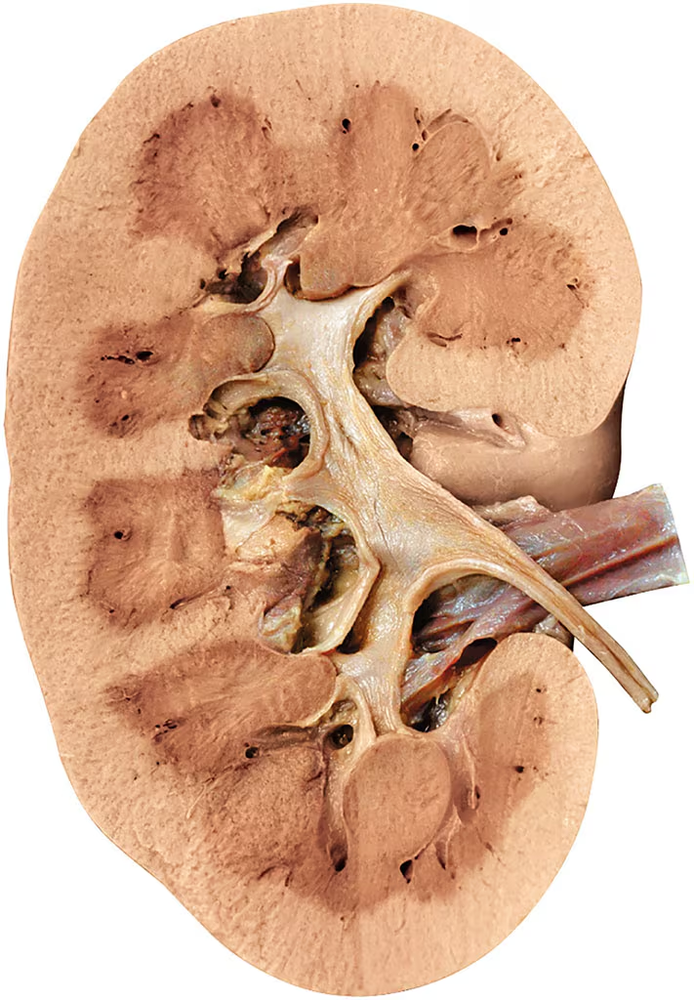
Problem 11
Using the image provided, identify and label the cortex, medulla, medullary pyramids, renal columns, and pelvis.
Problem 12
Trace the pathway a uric acid molecule takes from a glomerulus to the urethra. Name every gross or microscopic structure it passes through on its journey.
Problem 13
What is the function of the glomerulus?
Problem 15
Explain the difference between filtrate and urine.
Problem 16
How does aldosterone modify the chemical composition of urine?
Problem 20
Why is urinalysis a routine part of any good physical examination?
Problem 22
Define micturition, and describe the micturition reflex.
Problem 23
Contrast the following homeostatic imbalances: oliguria, anuria, polyuria, and nocturia.
Problem 24
Describe the changes that occur in kidney and bladder function in old age.
Problem 25
A 55-year-old woman is awakened by an excruciating pain that radiates from her right abdomen to her flank on the same side. The pain is not continuous, but it recurs every 3 to 4 minutes. Diagnose this patient's problem, and cite factors that might favor its occurrence. Explain why this woman's pain comes in 'waves.'
Problem 26
What happens to the rate of RBC production in a patient on dialysis with total renal failure? What could be given to the patient to counteract such a problem?
Problem 27
Two physiology students are having a disagreement about renal function. Dan says that the kidneys work harder when you eat a high-salt diet, whereas Peter says that they work harder when you drink lots of water. Who is right, and why?
Problem 28
Mr. Jessup, a 55-year-old man, is operated on for a cerebral tumor. About one month later, he complains that he is excessively thirsty and that he has been voiding almost continuously. A urine sample is collected, and its specific gravity is 1.001. What is your diagnosis of Mr. Jessup's problem, and how might it be related to his previous surgery?
Problem 29
Raymond is hypertensive and was recently diagnosed with impaired kidney function based on urinalysis and a blood test for creatinine. What sorts of test results would you expect, and how is hypertension related to kidney function?