Back
BackProblem 1
More than one choice may apply.
Which of the following are accessory sex structures in the male?
a. Gonads
b. Gametes
c. Broad shoulders
d. Seminal vesicles
Problem 2
In terms of development, which of these pairs is mismatched?
a. Vagina—penis
b. Testis—ovary
c. Labia majora—scrotum
d. Uterine tube—ductus deferens
Problem 3
More than one choice may apply.
The myometrium is the muscular layer of the uterus, and the endometrium is the_________layer.
a. serosa
b. adventitia
c. submucosa
d. mucosa
Problem 5
More than one choice may apply.
The approximate area between the anus and clitoris in the female is the
a. Peritoneum
b. Perineum
c. Vulva
d. Labia
Problem 6
More than one choice may apply.
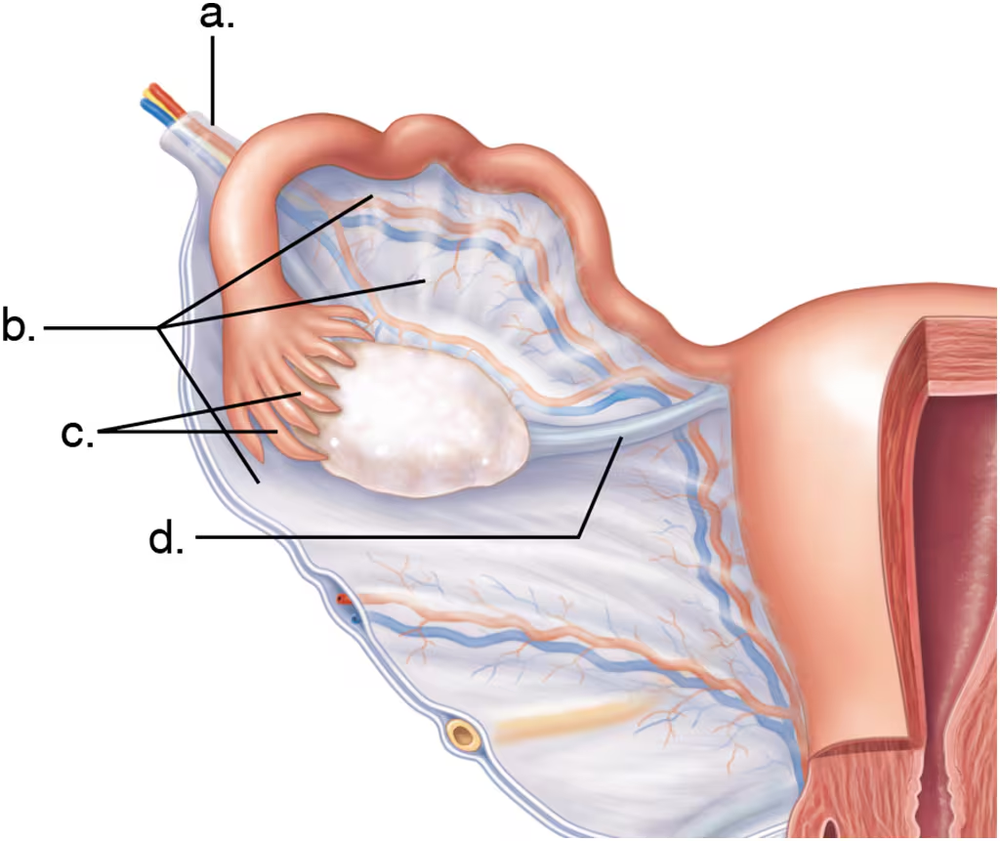
Which of the following attach to the ovary?
Problem 8
More than one choice may apply.
Select the false statement about the cervix of the uterus.
a. It is the superiormost part of the uterus.
b. It projects into the vagina.
c. Its cervical glands secrete mucus.
d. It contains the cervical canal.
Problem 11
More than one choice may apply.
The outer layer of the blastocyst, which attaches to the uterine wall, is the
a. Yolk sac
b. Inner cell mass
c. Amnion
d. Trophoblast
Problem 15
What are the primary sex organs, or gonads, of males? What are their two major functions?
Problem 16
What is the function of seminal fluid? Name the three types of glands that help produce it.
Problem 17
Why are the male gonads not found in the abdominal cavity? Where are they found?
Problem 21
Name the female gonad, and describe its two major functions.
Problem 22
Why is the term urogenital system more applicable to males than females?
Problem 23
Name the structures of the female duct system, and describe the important functions of each.
Problem 24
Given that the uterine tubes are not continuous with the ovaries, how can you explain the fact that not all ovulated 'eggs' end up in the female's peritoneal cavity?
Problem 34
Crystal had both her left ovary and her right uterine tube removed surgically at age 17 because of a cyst and a tumor in these organs. Now, at age 32, she remains healthy and is expecting her second child. How could Crystal conceive a child with just one ovary and one uterine tube, separated on opposite sides of the pelvis?