Back
BackProblem 1
A heat engine does 200 J of work per cycle while exhausting 400 J of waste heat. What is the engine's thermal efficiency?
Problem 3
A Boeing 777 jet engine, the world's largest, has a power output of 82 MW. It burns jet fuel with an energy density of 43 MJ /kg. What is the engine's fuel consumption rate, in kg/s, if its efficiency is 30%?
Problem 7
The power output of a car engine running at 2400 rpm is 500 kW. How much (a) work is done and (b) heat is exhausted per cycle if the engine's thermal efficiency is 20%? Give your answers in kJ.
Problem 11
A gas following the pV trajectory of FIGURE EX21.11 does 60 J of work per cycle. What is Vmax?
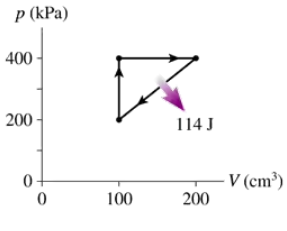
Problem 14
What are (a) Wout and QH and (b) the thermal efficiency for the heat engine shown in FIGURE EX21.14?
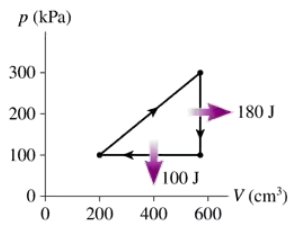
Problem 16
What are (a) the thermal efficiency and (b) the heat extracted from the hot reservoir for the heat engine shown in FIGURE EX21.16?
Problem 18
A 15 kW electric generator burns 1.2 gal of diesel fuel per hour. The energy density of diesel fuel is 140 MJ/gal. What is the generator's thermal efficiency?
Problem 19b
An air conditioner removes 5.0 x 10⁵ J/min of heat from a house and exhausts 8.0 x 10⁵ J/min to the hot outdoors. What is the air conditioner's coefficient of performance?
- The heat engine shown in FIGURE P21.62 uses 2.0 mol of a monatomic gas as the working substance. c. What is the engine's thermal efficiency?
Problem 21
Problem 21a
What are (a) the heat extracted from the cold reservoir and (b) the coefficient of performance for the refrigerator shown in FIGURE EX21.21?
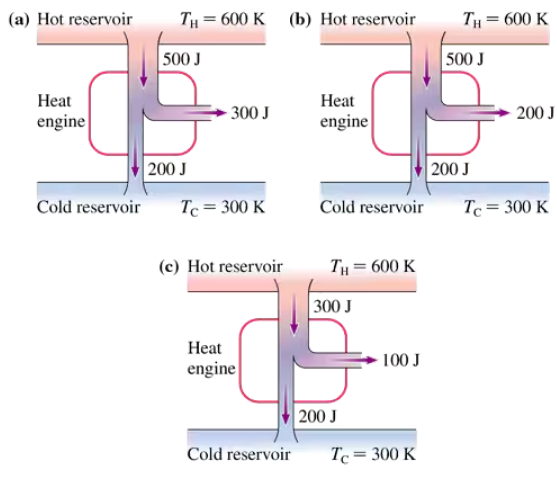
Problem 22
Which, if any, of the heat engines in FIGURE EX21.22 violate (a) the first law of thermodynamics or (b) the second law of thermodynamics? Explain.
Problem 24
At what cold-reservoir temperature (in ℃) would a Carnot engine with a hot-reservoir temperature of 427℃ have an efficiency of 60%?
Problem 27
A Carnot engine whose hot-reservoir temperature is 400℃ has a thermal efficiency of 40%. By how many degrees should the temperature of the cold reservoir be decreased to raise the engine's efficiency to 60%?
Problem 38
The engine that powers a crane burns fuel at a flame temperature of 2000℃. It is cooled by 20℃ air. The crane lifts a 2000 kg steel girder 30 m upward. How much heat energy is transferred to the engine by burning fuel if the engine is 40% as efficient as a Carnot engine?
Problem 39
A Carnot refrigerator operates between energy reservoirs at 0℃ and 250℃. A 2.4-cm-diameter, 50-cm-long copper bar connects the two energy reservoirs. At what rate, in W, must work be done on the refrigerator to remove heat from the cold reservoir at the same rate that it arrives through the copper bar?
Problem 41
An ideal refrigerator utilizes a Carnot cycle operating between 0℃ and 25℃. To turn 10 kg of liquid water at 0℃ into 10 kg of ice at 0℃, (a) how much heat is exhausted into the room and (b) how much energy must be supplied to the refrigerator?
Problem 42
A freezer with a coefficient of performance 30% that of a Carnot refrigerator keeps the inside temperature at -22℃ in a 25℃ room. 3.0 L of water at 20℃ are placed in the freezer. How long does it take for the water to freeze if the freezer's compressor does work at the rate of 200 W while the water is freezing?
Problem 44
A Carnot heat engine operates between reservoirs at 182℃ and 0℃. If the engine extracts 25 J of energy from the hot reservoir per cycle, how many cycles will it take to lift a 10 kg mass a height of 10 m?
Problem 45
A Carnot engine operates between temperatures of 5℃ and 500℃. The output is used to run a Carnot refrigerator operating between -5℃ and 25℃. How many joules of heat energy does the refrigerator exhaust into the room for each joule of heat energy used by the heat engine?
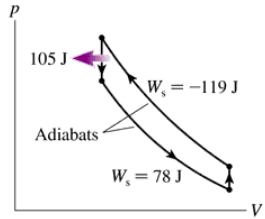
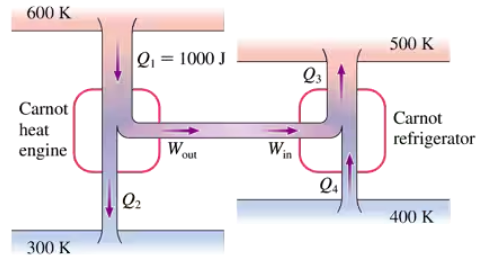
Problem 46a
FIGURE P21.46 shows a Carnot heat engine driving a Carnot refrigerator. Determine Q2, Q3 and Q4.
Problem 48
Home air conditioners in the United States have their power specified in the truly obscure units of tons, where 1 ton is the power needed to melt 1 ton (2000 lb or 910 kg) of ice in 24 hours. A modest-size house typically has a 4.0 ton air conditioner. If a 4.0 ton air conditioner has a coefficient of performance of 2.5, a typical value, at what rate in kW is heat energy removed from the house?
Problem 49
A car's internal combustion engine can be modeled as a heat engine operating between a combustion temperature of 1500℃ and an air temperature of 20℃ with 30% of the Carnot efficiency. The heat of combustion of gasoline is 47 kJ/g. What mass of gasoline is burned to accelerate a 1500 kg car from rest to a speed of 30 m/s?
Problem 51a
A typical coal-fired power plant burns 300 metric tons of coal every hour to generate 750 MW of electricity. 1 metric ton = 1000 kg. The density of coal is 1500 kg/m³ and its heat of combustion is 28 MJ/kg. Assume that all heat is transferred from the fuel to the boiler and that all the work done in spinning the turbine is transformed into electric energy. Suppose the coal is piled up in a 10 m ✕ 10 m room. How tall must the pile be to operate the plant for one day?
Problem 52b
A nuclear power plant generates 3000 MW of heat energy from nuclear reactions in the reactor's core. This energy is used to boil water and produce high-pressure steam at 300℃. The steam spins a turbine, which produces 1000 MW of electric power, then the steam is condensed and the water is cooled to 25℃ before starting the cycle again. What is the plant's actual efficiency?
Problem 55a
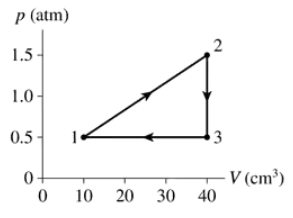
A heat engine using a diatomic gas follows the cycle shown in FIGURE P21.55. Its temperature at point 1 is 20℃. Determine Ws, Q, and ∆Eth for each of the three processes in this cycle. Display your results in a table.
Problem 57a
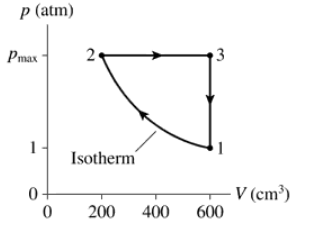
FIGURE P21.57 shows the cycle for a heat engine that uses a gas having γ = 1.25. The initial temperature is T1 = 300 K, and this engine operates at 20 cycles per second. What is the power output of the engine?
Problem 59a
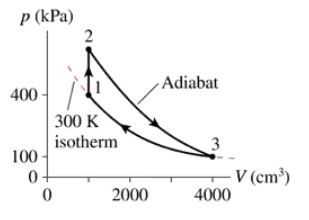
A heat engine uses a diatomic gas that follows the pV cycle in FIGURE P21.59. Determine the pressure, volume, and temperature at point 2.
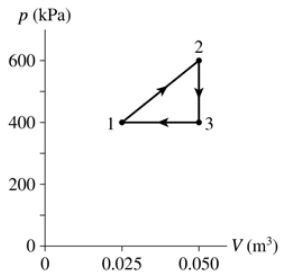
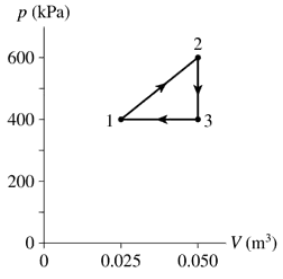
Problem 62a
The heat engine shown in FIGURE P21.62 uses 2.0 mol of a monatomic gas as the working substance. Determine T1, T2 and T3.
Problem 62b
The heat engine shown in FIGURE P21.62 uses 2.0 mol of a monatomic gas as the working substance. Make a table that shows ∆Eth, Ws, and Q for each of the three processes.
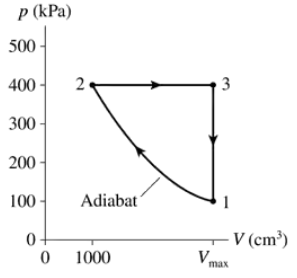
Problem 63b
The heat engine shown in FIGURE P21.63 uses 0.020 mol of a diatomic gas as the working substance. Make a table that shows ∆Eth, Ws, and Q for each of the three processes.