Back
BackProblem 1
3.5×1010 electrons are added to a plastic rod by rubbing it with wool. What is the charge on the rod?
Problem 3a
A plastic rod that has been charged to −15 nC touches a metal sphere. Afterward, the rod's charge is −10 nC. What kind of charged particle was transferred between the rod and the sphere, and in which direction? That is, did it move from the rod to the sphere or from the sphere to the rod?
Problem 3b
A plastic rod that has been charged to −15 nC touches a metal sphere. Afterward, the rod's charge is −10 nC. How many charged particles were transferred?
Problem 4b
A glass rod that has been charged to +12 nC touches a metal sphere. Afterward, the rod’s charge is +8.0 nC. How many charged particles were transferred?
Problem 5
What is the total charge of all the electrons in L of liquid water?
Problem 6
What mass of aluminum has a total nuclear charge of C? Aluminum has atomic number .
Problem 7
A linear accelerator uses alternating electric fields to accelerate electrons to close to the speed of light. A small number of the electrons collide with a target, but a large majority pass through the target and impact a beam dump at the end of the accelerator. In one experiment the beam dump measured charge accumulating at a rate of −2.0 nC/s. How many electrons traveled down the accelerator during the 2.0 h run?
Problem 9
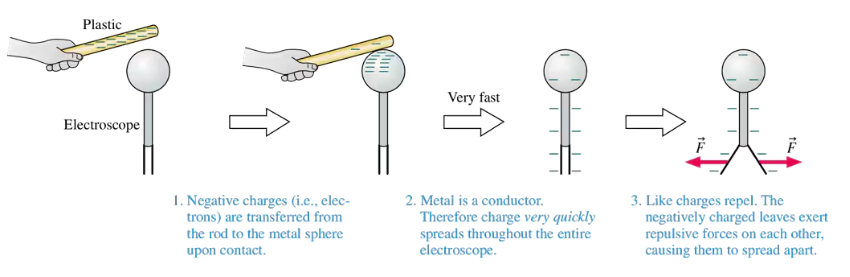
Figure 22.8 showed how an electroscope becomes negatively charged. The leaves will also repel each other if you touch the electroscope with a positively charged glass rod. Use a series of charge diagrams to explain what happens and why the leaves repel each other.
Problem 14a
Two small plastic spheres each have a mass of 2.0 g and a charge of −50.0 nC. They are placed 2.0 cm apart (center to center). What is the magnitude of the electric force on each sphere?
Problem 15b
Two protons are 2.0 fm apart. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on one proton due to the other proton?
Problem 17
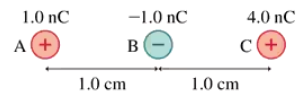
What is the magnitude of the net force on charge A in FIGURE EX22.17?
Problem 20
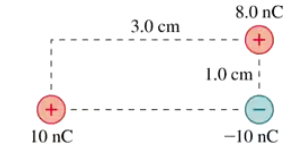
What is the force F on the 1.0 nC charge in FIGURE EX22.20? Give your answer as a magnitude and a direction.
Problem 22a
A 2.0 g plastic bead charged to −4.0 nC and a 4.0 g glass bead charged to +8.0 nC are 2.0 cm apart and free to move. What are the accelerations of the plastic bead?
Problem 24
A massless spring is attached to a support at one end and has a 2.0 μC charge glued to the other end. A −4.0 μC charge is slowly brought near. The spring has stretched 1.2 cm when the charges are 2.6 cm apart. What is the spring constant of the spring?
Problem 27a
What are the strength and direction of the electric field 1.0 mm from a proton?
Problem 29a
The electric field at a point in space is N/C. What is the electric force on a proton at this point? Give your answer in component form.
Problem 29d
The electric field at a point in space is N/C. What is the magnitude of the electron’s acceleration?
Problem 32
A charge is located at . What are the electric fields at the positions , and ? Write each electric field vector in component form.
Problem 34b
A 0.10 g honeybee acquires a charge of +23 pC while flying. What electric field (strength and direction) would allow the bee to hang suspended in the air?
Problem 37
Two 1.0 g spheres are charged equally and placed 2.0 cm apart. When released, they begin to accelerate at 150 m/s2. What is the magnitude of the charge on each sphere?
Problem 39
A 3.00-cm-long spring has a small plastic bead glued to each end. Charging each bead to −25 nC expands the spring by 0.50 cm. What is the value of the spring constant?
Problem 42a
Objects A and B are both positively charged. Both have a mass of 100 g, but A has twice the charge of B. When A and B are placed 10 cm apart, B experiences an electric force of 0.45 N. What is the charge on A?
Problem 44
What is the force F on the 8.0 nC charge in FIGURE P22.44? Give your answer as a magnitude and an angle measured cw or ccw (specify which) from the +x-axis.
Problem 47
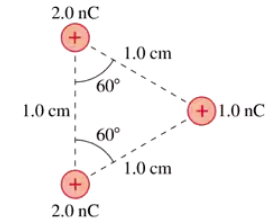
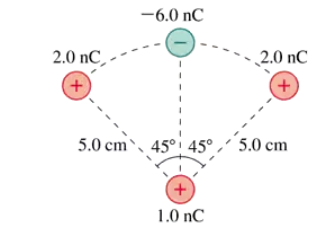
What is the force F on the 1.0 nC charge at the bottom in FIGURE P22.47? Give your answer in component form.
Problem 49b
A +2.0 nC charge is at the origin and a −4.0 nC charge is at x = 1.0 cm. Would the net force be zero for an electron placed at the same position? Explain.
Problem 52
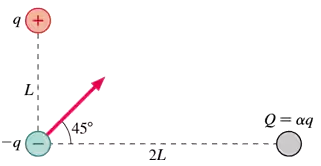
FIGURE P22.52 shows three charges and the net force on charge −q. Charge Q is some multiple α of q. What is α?
Problem 55
In a simple model of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves in a circular orbit of radius 0.053 nm around a stationary proton. How many revolutions per second does the electron make?
Problem 57
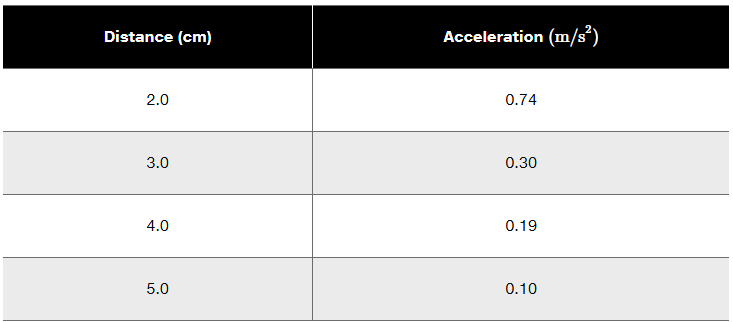
You have two small, 2.0 g balls that have been given equal but opposite charges, but you don't know the magnitude of the charge. To find out, you place the balls distance apart on a slippery horizontal surface, release them, and use a motion detector to measure the initial acceleration of one of the balls toward the other. After repeating this for several different separation distances, your data are shown below. Use an appropriate graph of the data to determine the magnitude of the charge.
Problem 59
Two equal point charges 2.5 cm apart, both initially neutral, are being charged at the rate of 5.0 nC/s. At what rate (N/s) is the force between them increasing 1.0 s after charging begins?
Problem 60
You have a lightweight spring whose unstretched length is 4.0 cm. First, you attach one end of the spring to the ceiling and hang a 1.0 g mass from it. This stretches the spring to a length of 5.0 cm. You then attach two small plastic beads to the opposite ends of the spring, lay the spring on a frictionless table, and give each plastic bead the same charge. This stretches the spring to a length of 4.5 cm. What is the magnitude of the charge (in nC) on each bead?