Back
BackProblem 41c
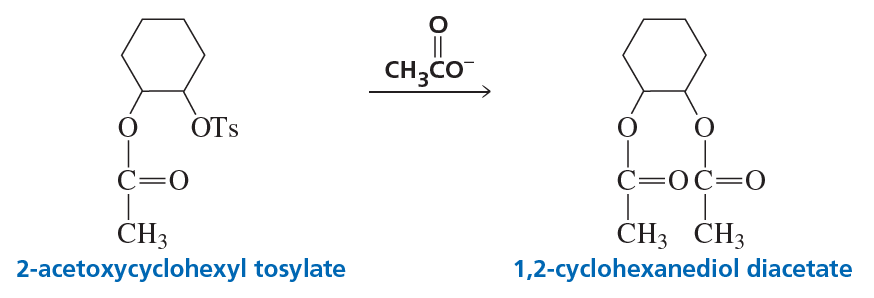
2-Acetoxycyclohexyl tosylate reacts with acetate ion to form 1,2-cyclohexanediol diacetate. The reaction is stereospecific—that is, the stereoisomers obtained as products depend on the stereoisomer used as a reactant. Recall that because 2-acetoxycyclohexyl tosylate has two asymmetric centers, it has four stereoisomers—two are cis and two are trans. Explain the following observations:
c. A trans reactant is more reactive than a cis reactant.
Problem 42
Proof that an imine was formed between aldolase and its substrate was obtained by using D-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate labeled at the C-2 position with 14C as the substrate. NaBH4 was added to the reaction mixture. A radioactive product was isolated from the reaction mixture and hydrolyzed in an acidic solution. Draw the structure of the radioactive product obtained from the acidic solution. (Hint: NaBH4 reduces an imine linkage.)
Problem 43a
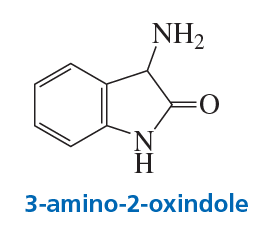
3-Amino-2-oxindole catalyzes the decarboxylation of a-keto acids.
a. Propose a mechanism for the catalyzed reaction.
Problem 44a
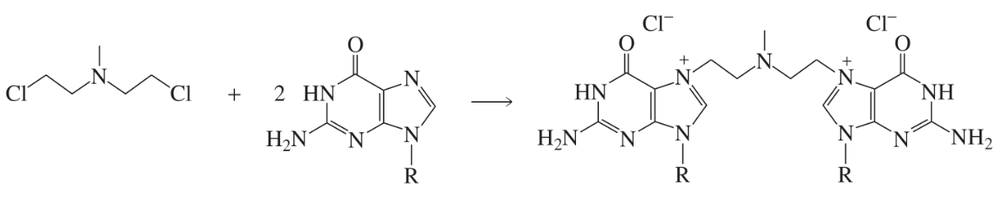
Explain why the alkyl halide shown here reacts much more rapidly with guanine than does a primary alkyl halide (such as pentyl chloride).
Problem 45
Triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) catalyzes the conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. The enzyme’s catalytic groups are Glu 165 and His 95. In the first step of the reaction, these catalytic groups function as a general-base and a general-acid catalyst, respectively. Propose a mechanism for the reaction.