Back
BackProblem 1
In practical terms in everyday use, which of the following statements provides the definition of sterilization?
a. Sterilization eliminates all organisms and viruses
b. Sterilization eliminates harmful microorganisms and viruses
c. Sterilization eliminates prions
d. Sterilization eliminates hyperthermophiles
Problem 1
Describe three types of microbes that are extremely resistant to antimicrobial treatment, and explain why they are resistant.
Problem 1
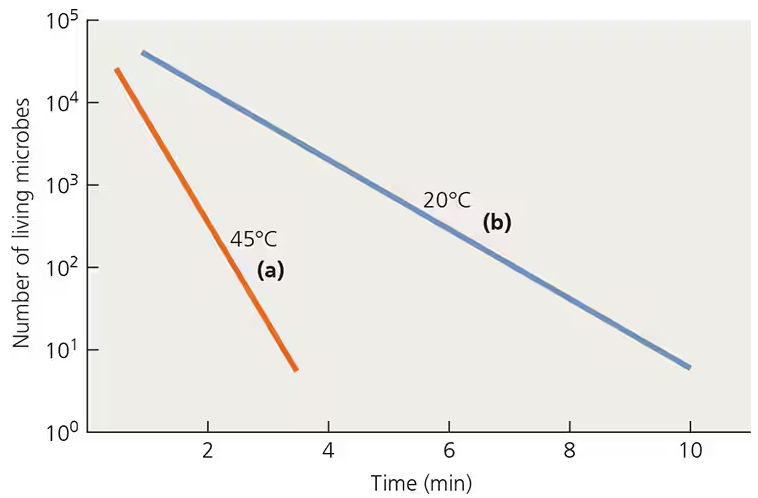
Calculate the decimal reduction time (D) for the two temperatures in the following graph.
Problem 2
Compare and contrast four tests that have been developed to measure the effectiveness of disinfectants.
Problem 2
Which of the following substances or processes kills microorganisms on laboratory surfaces?
a. Antiseptics
b. Disinfectants
c. Degermers
d. Pasteurization
Problem 3
Which of the following terms best describes the disinfecting of cafeteria plates?
a. Pasteurization
b. Antisepsis
c. Sterilization
d. Sanitization
Problem 3
Why is it necessary to use strong disinfectants in areas exposed to tuberculosis patients?
Problem 4
Why do warm disinfectant chemicals generally work better than cool ones?
Problem 4
The microbial death rate is used to measure the effectiveness of:
a. A detergent
b. An antiseptic
c. Sanitization techniques
d. All of the above
Problem 5
Why are Gram-negative bacteria more susceptible to heat than Gram-positive bacteria?
Problem 5
Which of the following statements is true concerning the selection of an antimicrobial agent?
a. An ideal antimicrobial agent is stable during storage
b. An ideal antimicrobial agent is fast acting
c. Ideal microbial agents do not exist
d. All of the above are correct
Problem 6
Describe five physical methods of microbial control.
Problem 6
The endospores of which organism can be used as a biological indicator of sterilization?
a. Bacillus stearothermophilus
b. Salmonella enterica
c. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
d. Staphylococcus aureus
Problem 7
A company that manufactures an antimicrobial cleaner for kitchen counters claims that its product is effective when used in a 50% water solution. By what means might scientists best verify this statement?
a. Disk-diffusion test
b. Phenol coefficient
c. Filter paper test
d. In-use test
Problem 7
What is the difference between thermal death point and thermal death time?
Problem 8
Defend the following statement: “Pasteurization is not sterilization.”
Problem 8
Which of the following items functions most like an autoclave?
a. Boiling pan
b. Incinerator
c. Microwave oven
d. Pressure cooker
Problem 9
Compare and contrast desiccation and lyophilization.
Problem 9
The preservation of beef jerky from microbial growth relies on which method of microbial control?
a. Filtration
b. Lyophilization
c. Desiccation
d. Radiation
Problem 10
Which of the following types of radiation is more widely used as an antimicrobial technique?
a. Electron beams
b. Visible light waves
c. Radio waves
d. Microwaves
Problem 10
Compare and contrast the action of alcohols, halogens, and oxidizing agents in controlling microbial growth.
Problem 11
Which of the following substances would most effectively inhibit anaerobes?
a. Phenol
b. Silver
c. Ethanol
d. Hydrogen peroxide
Problem 11
Hyperthermophilic prokaryotes may remain viable in canned goods after commercial sterilization. Why is this situation not dangerous to consumers?
Problem 12
Which of the following adjectives best describes a surgical procedure that is free of microbial contaminants?
a. Disinfected
b. Sanitized
c. Degermed
d. Aseptic
Problem 12
Why are alcohols more effective in a 70% solution than in a 100% solution?
Problem 13
Biosafety Level 3 includes:
a. Double sets of entry doors
b. Pressurized suits
c. Showers in entryways
d. All of the above
Problem 13
Contrast the structures and actions of soaps and quats.
Problem 14
What are some advantages and disadvantages of using ionizing radiation to sterilize food?
Problem 14
A sample of E. coli has been subjected to heat for a specified time, and 90% of the cells have been destroyed. Which of the following terms best describes this event?
a. Thermal death point
b. Thermal death time
c. Decimal reduction time
d. None of the above
Problem 15
How can campers effectively treat stream water to remove pathogenic protozoa, bacteria, and viruses?