Back
BackProblem 1
How does the genotype of a bacterium determine its phenotype? Use the terms gene, mRNA, ribosome, and polypeptide in your answer.
Problem 1
Which of the following is most likely the number of base pairs in a bacterial chromosome?
a. 4,000,000
b. 4000
c. 400
d. 40
Problem 1
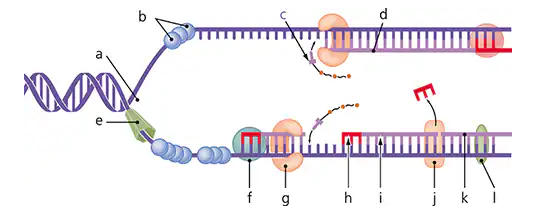
On the accompanying figure, label:
DNA polymerase I, DNA polymerase III, helicase, lagging strand, leading strand, ligase, nucleotide (triphosphate), Okazaki fragment, primase, replication fork, RNA primer, and stabilizing proteins.
Problem 1
The three steps in RNA transcription are __________ , ___________ , and __________ .
Problem 2
List several ways in which eukaryotic messenger RNA differs from prokaryotic mRNA.
Problem 2
A triplet of mRNA nucleotides that specifies a particular amino acid is called a ____________ .
Problem 2
Which of the following is a true statement concerning prokaryotic chromosomes?
a. They typically have two or three origins of replication
b. They contain single-stranded DNA
c. They are located in the cytosol
d. They are associated in linear pairs
Problem 2
This bacteriophage DNA molecule has been warmed. Label the portions that likely have a higher ratio of GC base pairs and the portions that have a higher ratio of AT base pairs.
Problem 3
A plasmid is __________ .
a. a molecule of RNA found in bacterial cells
b. distinguished from a chromosome by being circular
c. a structure in bacterial cells formed from plasma membrane
d. extrachromosomal DNA
Problem 3
Three effects of point mutations are ___________ , ___________ , and ____________ .
Problem 3
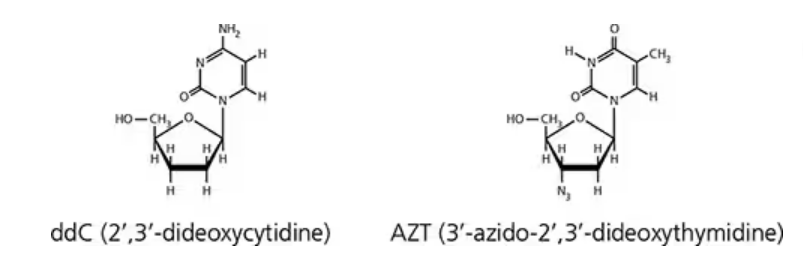
The drugs ddC and AZT are used to treat AIDS.
Based on their chemical structures, what is their mode of action?
Problem 3
Compare and contrast introns and exons.
Problem 4
Which of the following forms ionic bonds with eukaryotic DNA and stabilizes it?
a. Chromatin
b. Bacteriocin
c. Histone
d. Nucleoid
Problem 4
Polypeptide synthesis requires large amounts of energy. How do cells regulate synthesis to conserve energy? Describe one specific example.
Problem 4
Insertions and deletions in the genetic code are also called ___________ mutations.
Problem 5
An operon consists of __________ , ___________ , and __________ , and is associated with a regulatory gene.
Problem 5
Nucleotides used in the replication of DNA __________ .
a. Carry energy
b. Are found in four forms, each with a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a base
c. Are present in cells as triphosphate nucleotides
d. All of the above are correct.
Problem 5
Describe the operon model of gene regulation.
Problem 6
In general, __________ operons are inactive until the substrate of their genes’ polypeptides is present.
Problem 6
Which of the following molecules functions as a “proofreader” for a newly replicated strand of DNA?
a. DNA polymerase III
b. Primase
c. Helicase
d. Ligase
Problem S6
Compare and contrast the structure and components of DNA and RNA in prokaryotes.
Problem 7
The addition of a ----CH3 to a cytosine nucleotide after DNA replication is called: .
a. Methylation
b. Restriction
c. Transcription
d. Transversion
Problem 7
A daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand because DNA replication is __________ .
Problem 7
Besides the fact that it synthesizes RNA, how does RNA polymerase differ in function from DNA polymerase?
Problem 8
Describe the formation and function of mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Problem 8
A gene for antibiotic resistance can move horizontally among bacterial cells by __________ , __________ , and __________ .
Problem 8
In translation, the site through which tRNA molecules leave a ribosome is called the:
a. A site
b. X site
c. P site
d. E site
Problem 9
__________ are nucleotide sequences containing palindromes and genes for proteins that cut DNA strands.
Problem 9
Describe how DNA is packaged in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Problem 9
The Ames test ___________.
a. uses auxotrophs and liver extract to reveal mutagens
b. s time intensive and costly
c. involves the isolation of a mutant by eliminating wild-type phenotypes with specific media
d. proves that suspected chemicals are carcinogenic