Back
BackProblem 1
The final electron acceptor in cyclic photophosphorylation is _________.
Problem 1
How does amination differ from transamination?
Problem 1
For the phrase given below, indicate the type of metabolism referred to, using the following choices:
a. Anabolism only
b. Both anabolism and catabolism (amphibolic)
c. Catabolism only
Breaks a large molecule into smaller ones
Problem 1
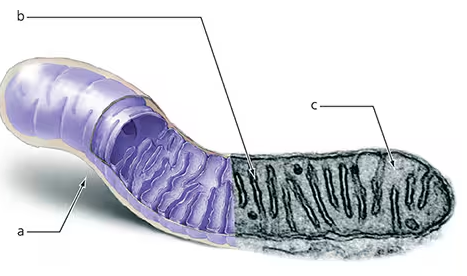
Label the mitochondrion to indicate the location of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and electron transport chains.
Problem 1
Match the descriptions below with their corresponding terms.
1. _____ Occurs when energy from a compound containing phosphate reacts with ADP to form ATP
2. _____ Involves formation of ATP via reduction of coenzymes in the electron transport chain
3. _____ Begins with glycolysis
4. _____ Occurs when all active sites on substrate molecules are filled
A. Saturation
B. Oxidative phosphorylation
C. Substrate-level phosphorylation
D. Photophosphorylation
E. Carbohydrate catabolism
Problem 2
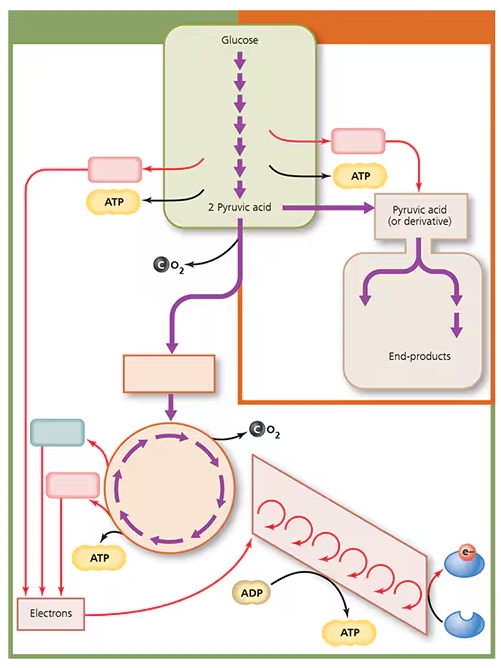
Label the diagram below to indicate acetyl-CoA, electron transport chain, FADH2, fermentation, glycolysis, citric acid cycle, NADH, and respiration. Indicate the net number of molecules of ATP that could be synthesized at each stage during bacterial respiration of one molecule of glucose.
Problem 2
For the phrase given below, indicate the type of metabolism referred to, using the following choices:
a. Anabolism only
b. Both anabolism and catabolism (amphibolic)
c. Catabolism only
Includes dehydration synthesis reactions
Problem 2
Two ATP molecules are used to initiate glycolysis. Enzymes generate molecules of ATP for each molecule of glucose that undergoes glycolysis. Thus, a net gain of _________ molecules of ATP is produced in glycolysis.
Problem 2
Why are enzymes necessary for anabolic reactions to occur in living organisms?
Problem V2
Indian tradition holds that storing water in brass pitchers prevents disease. Scientists have discovered that there is some truth in the tradition. The researchers collected river water samples and found fecal bacterial counts as high as 1 million bacteria per milliliter. However, they could detect no bacteria in the water after it had been stored for two days in traditional brass pitchers. Bacterial levels in plastic or earthenware containers remained high over the same period. How can brass, which is an alloy of copper mixed with zinc, make water safer to drink?
<IMAGE>
Problem 3
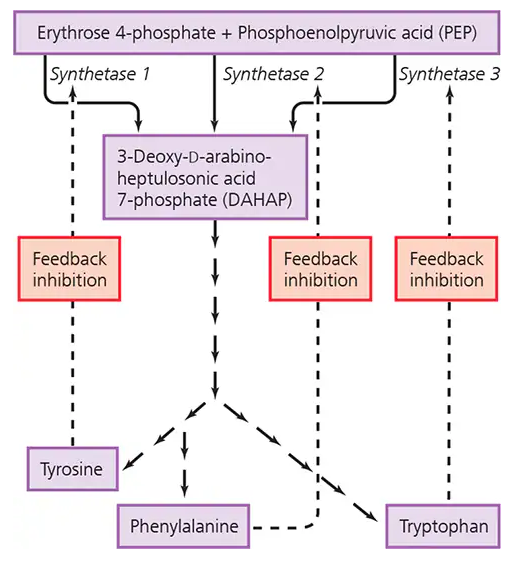
Examine the biosynthetic pathway for the production of the amino acids tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine in the figure. Where do the initial reactants (erythrose 4-phosphate and PEP) originate?
Problem 3
For the phrase given below, indicate the type of metabolism referred to, using the following choices:
a. Anabolism only
b. Both anabolism and catabolism (amphibolic)
c. Catabolism only
Is exergonic
Problem 3
How do organisms control the rate of metabolic activities in their cells?
Problem 3
The initial catabolism of glucose occurs by glycolysis and/or the ________ and ________pathways.
Problem 4
For the phrase given below, indicate the type of metabolism referred to, using the following choices:
a. Anabolism only
b. Both anabolism and catabolism (amphibolic)
c. Catabolism only
Is endergonic
Problem 4
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor at a single allosteric site affect a whole pathway of enzymatic reactions?
Problem 4
_______ is a cyclic series of eight reactions involved in the catabolism of acetyl-CoA that yields eight molecules of NADH and two molecules of FADH2.
Problem 5
The final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is ________.
Problem 5
For the phrase given below, indicate the type of metabolism referred to, using the following choices:
a. Anabolism only
b. Both anabolism and catabolism (amphibolic)
c. Catabolism only
Involves the production of cell membrane constituents
Problem 5
Explain the mechanism of negative feedback with respect to enzyme action.
Problem 6
For the phrase given below, indicate the type of metabolism referred to, using the following choices:
a. Anabolism only
b. Both anabolism and catabolism (amphibolic)
c. Catabolism only
Includes hydrolytic reactions
Problem 6
Facultative anaerobes can live under either aerobic or anaerobic conditions. What metabolic pathways allow these organisms to continue to harvest energy from sugar molecules in the absence of oxygen?
Problem 6
Photosynthetic bacteria that also fix nitrogen are:
a. Mycoplasmas
b. Spirilla
c. Bacteroids
d. Cyanobacteria
Problem 6
Three common inorganic electron acceptors in anaerobic respiration are _______,_______, and _______.
Problem 7
For the phrase given below, indicate the type of metabolism referred to, using the following choices:
a. Anabolism only
b. Both anabolism and catabolism (amphibolic)
c. Catabolism only
Includes metabolism
Problem 7
Anaerobic respiration typically uses (organic/inorganic)________ molecules as final electron acceptors.
Problem 7
How does oxidation of a molecule occur without oxygen?
Problem 8
List at least four groups of microorganisms that are photosynthetic.
Problem 8
Redox reactions ______.
a. Transfer energy
b. Transfer electrons
c. Involve oxidation and reduction
d. Are involved in all of the above
Problem 8
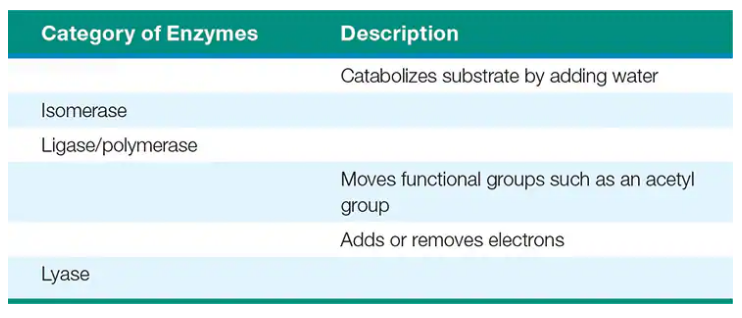
Complete the following chart:
The main coenzymes that carry electrons in catabolic pathways are _______ and ________.