Back
BackProblem 1
If an objective magnifies 40× and each binocular lens magnifies 15×, the total magnification of the object being viewed is ________.
Problem 1
Explain how the principle, “electrons travel as waves,” applies to microscopy.
Problem 1
Which of the following is smallest?
a. decimeter
d. millimeter
c. nanometer
d. micrometer
Problem 1
Label each photograph with the type of microscope used to acquire the image.
a. _______<IMAGE>
b. _______<IMAGE>
c. _______<IMAGE>
d. _______<IMAGE>
e. _______<IMAGE>
f. _______<IMAGE>
Problem 2
A nanometer is _______ than a micrometer.
a. 10 times larger
b. 10 times smaller
c. 1000 times larger
d. 1000 times smaller
Problem 2
Critique the following definition of magnification given by a student on a microbiology test: “Magnification makes things bigger.”
Problem 2
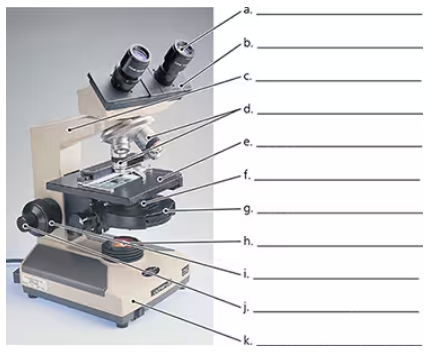
Label the microscope.
Problem 2
The type of fixation developed by Koch for bacteria is _______.
Problem 3
Immersion oil ________(increases/decreases) the numerical aperture, which ________(increases/decreases) resolution because _______(more/fewer) light rays are involved.
Problem 3
Resolution is best described as the ____________.
a. Ability to view something that is small
b. Ability to magnify a specimen
c. Ability to distinguish between two adjacent objects
d. Difference between two waves of electromagnetic radiation
Problem 3
Why can electron microscopes magnify only dead organisms?
Problem 4
Put the following substances in the order they are used in a Gram stain:
Counterstain
Decolorizing agent
Mordant
Primary stain
Problem 4
Curved glass lenses _______light.
a. Refract
b. Bend
c. Magnify
d. Both a and b
Problem 4
________ refers to differences in intensity between two objects.
Problem 5
Cationic chromophores such as methylene blue ionically bond to _______(positively/negatively) charged chemicals such as DNA and proteins.
Problem 5
Why is Latin used in taxonomic nomenclature?
Problem 5
Which of the following factors is important in making an image appear larger?
a. Thickness of the lens
b. Curvature of the lens
c. Speed of the light passing through the lens
d. All of the above
Problem 6
Give three characteristics of a “specific epithet.”
Problem 6
Which of the following is different between light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy?
a. Magnification
b. Resolution
c. Wavelengths
d. All of the above
Problem 7
How does the study of the nucleotide sequences of ribosomal RNA fit into a discussion of taxonomy?
Problem 7
Which of the following types of microscopes produces a three- dimensional image with a shadowed appearance?
a. Simple microscope
b. Differential interference contrast microscope
c. Fluorescence microscope
d. Transmission electron microscope
Problem 8
An atomic force microscope can magnify a living cell, whereas electron microscopes and scanning tunneling microscopes cannot. What requirement of scanning tunneling microscopes precludes the imaging of living specimens?
Problem 8
Which of the following microscopes combines the greatest magnification with the best resolution?
a. Confocal microscope
b. Phase-contrast microscope
c. Dark-field microscope
d. Bright-field microscope
Problem 9
Negative stains such as eosin are also called _______.
a. Capsule stains
b. Endospore stains
c. Simple stains
d. Acid-fast stains
Problem 10
In the binomial system of nomenclature, which term is always written in lowercase letters?
a. Kingdom
b. Domain
c. Genus
d. Specific epithet