Which of the following molecules will produce the most ATP per mole?
a. glucose or stearic acid (C18)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
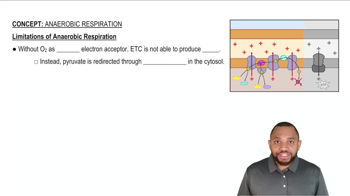

Which of the following molecules will produce the most ATP per mole?
a. glucose or stearic acid (C18)
Match the following ATP yields to reactions a to g:
1.5 ATP 2.5 ATP 7 ATP 10 ATP
12 ATP 32 ATP 36 ATP
f. NADH + H+ is oxidized to NAD+.
Identify each of the following reactions a to e in the β oxidation of palmitic acid, a C16 fatty acid, as
(1) activation
(2) first oxidation
(3) hydration
(4) second oxidation
(5) cleavage
a. Palmitoyl CoA and FAD form α, β-unsaturated palmitoyl CoA and FADH2.
Identify each of the following reactions a to e in the β oxidation of palmitic acid, a C16 fatty acid, as
(1) activation
(2) first oxidation
(3) hydration
(4) second oxidation
(5) cleavage
c. Palmitic acid, CoA, and ATP form palmitoyl CoA.
Which of the following molecules will produce the most ATP per mole?
d. glucose or caprylic acid (C8)