What is the difference in hydrogen bonding between an α helix and a β−pleated sheet?

What type of interaction would you expect between the R groups of the following amino acids in a quaternary structure?
d. alanine and proline
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
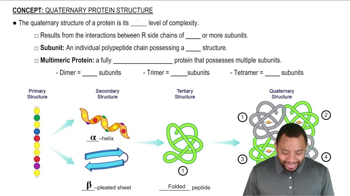
Quaternary Structure of Proteins
R Groups of Amino Acids
Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Interactions
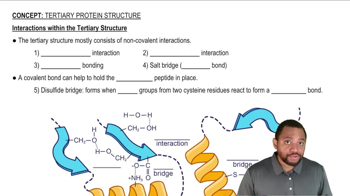
What type of interaction would you expect between the R groups of the following amino acids in a tertiary structure?
c. serine and aspartate
What type of interaction would you expect between the R groups of the following amino acids in a quaternary structure?
a. phenylalanine and isoleucine
A portion of a polypeptide chain contains the following sequence of amino acids:
—Leu—Val—Cys—Asp—
a. Which amino acids are likely to be found on the inside of the protein structure? Why?
A portion of a polypeptide chain contains the following sequence of amino acids:
—Leu—Val—Cys—Asp—
c. How does the primary structure of a protein affect its tertiary structure?
In myoglobin, about one-half of the 153 amino acids have nonpolar R groups.
a. Where would you expect those amino acids to be located in the tertiary structure?
