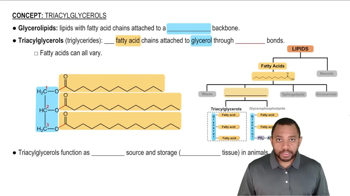
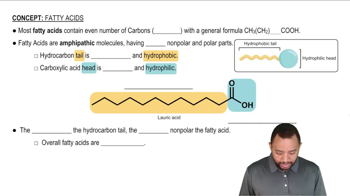
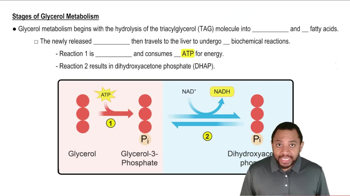
Textbook Question
The total kilocalories and grams of fat for some typical meals at fast-food restaurants are listed here. Calculate the number of kilocalories and the percentage of total kilocalories from fat (1 gram of fat = 9 kcal). Round kcals to the tens place.
a. a beef burrito, 470 kcal, 21 g of fat