Identify each of the following properties as more typical of an organic or inorganic compound:
b. is a gas at room temperature

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

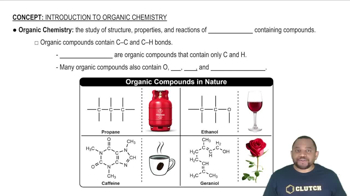

Identify each of the following properties as more typical of an organic or inorganic compound:
b. is a gas at room temperature
Identify each of the following as a formula of an organic or inorganic compound. For an organic compound, indicate if represented as molecular formula, expanded, or condensed structural formula:
b. K3PO4
Identify each of the following as a formula of an organic or inorganic compound. For an organic compound, indicate if represented as molecular formula, expanded, or condensed structural formula:
d.
Identify each of the following as a formula of an organic or inorganic compound. For an organic compound, indicate if represented as molecular formula, expanded, or condensed structural formula:
e. CH3―CH2―CH2―CH2―CH3
Identify each of the following properties as more typical of an organic or inorganic compound:
c. contains carbon and hydrogen
Identify each of the following properties as more typical of an organic or inorganic compound:
c. contains covalent bonds