Consider the following segment of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
ACA UCA CGG GUA
a. What is the amino acid order produced from this mRNA?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
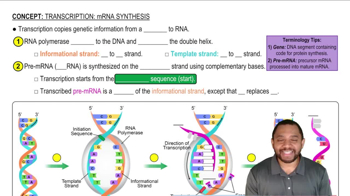

Consider the following segment of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
ACA UCA CGG GUA
a. What is the amino acid order produced from this mRNA?
Consider the following segment of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
ACA UCA CGG GUA
b. What is the amino acid order if a point mutation changes UCA to ACA?
Consider the following segment of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
ACA UCA CGG GUA
e. What is the amino acid order if an insertion mutation adds a G to the beginning of the mRNA segment?
A point mutation changes a codon in the mRNA for an enzyme from GCC to GCA. Why is there no change in the amino acid order in the protein?
In sickle-cell anemia, a point mutation in the mRNA for hemoglobin results in the replacement of glutamate with valine in the resulting hemoglobin molecule. Why does the replacement of one amino acid cause such a drastic change in biological function?
A point mutation in the mRNA for an enzyme results in the replacement of leucine with alanine in the resulting enzyme molecule. Why does this change in amino acids have little effect on the biological activity of the enzyme?