What is the effect of a deletion mutation on the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide?

Consider the following segment of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
ACA UCA CGG GUA
b. What is the amino acid order if a point mutation changes UCA to ACA?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
mRNA Translation
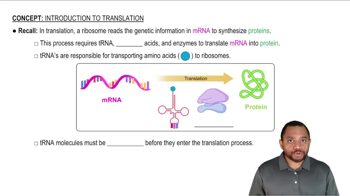
Point Mutation

Amino Acid Codons

How is protein synthesis affected if the normal base sequence TTT in the DNA template strand is changed to TTC?
Consider the following segment of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
ACA UCA CGG GUA
a. What is the amino acid order produced from this mRNA?
Consider the following segment of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
ACA UCA CGG GUA
e. What is the amino acid order if an insertion mutation adds a G to the beginning of the mRNA segment?
Consider the following segment of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
ACA UCA CGG GUA
f. What is the amino acid order if a deletion mutation removes the A at the beginning of the mRNA segment?
A point mutation changes a codon in the mRNA for an enzyme from GCC to GCA. Why is there no change in the amino acid order in the protein?
