Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products of the following:
d.

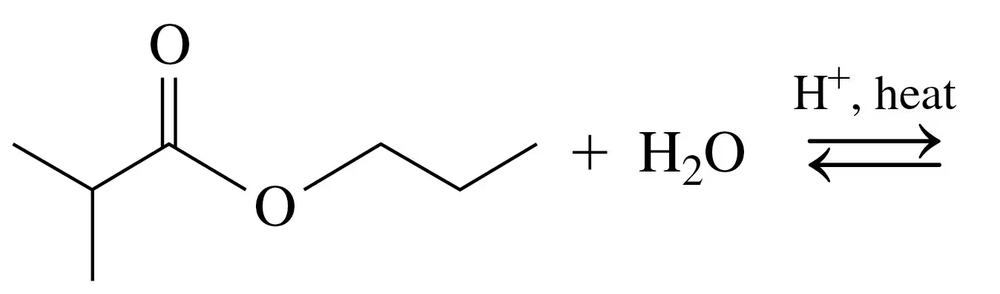
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products of the following:
d.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products of the following:
c.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products of the following:
a.
Write the common name and classify each of the following compounds as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°): (14.5)
a.
Write the common name and classify each of the following compounds as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°):
b.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula if cyclic, for each of the following:
b. cyclohexylamine