Textbook Question
Indicate if each of the following is soluble in water. Explain.
b.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
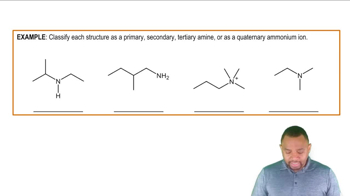

Indicate if each of the following is soluble in water. Explain.
b.
Indicate if each of the following is soluble in water. Explain.
c.
Indicate if each of the following is soluble in water. Explain.
d.
Write the balanced chemical equations for the (1) reaction of each of the following amines with water and (2) neutralization with HBr:
b. propylamine
Write the balanced chemical equations for the (1) reaction of each of the following amines with water and (2) neutralization with HBr:
c. N-methylaniline
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula for the amide formed in each of the following reactions:
a.