Textbook Question
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alcohols and phenols:
a.

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones Problem 46c
Problem 46c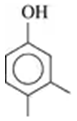
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alcohols and phenols:
a.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alcohols and phenols:
c.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alcohols and phenols:
b.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula for each of the following:
b. 2-methyl-3-pentanol
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula for each of the following:
c. methyl propyl ether
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula for each of the following:
d. 2,4-dibromophenol