Draw the condensed structural formula for the alcohol formed when each of the following is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst:
a. butyraldehyde

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones Problem 34a
Problem 34a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
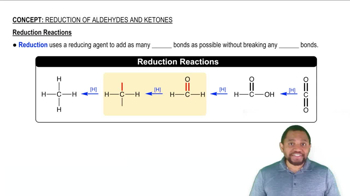
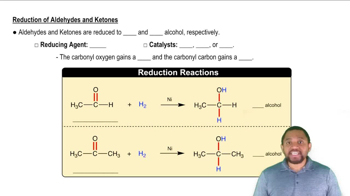
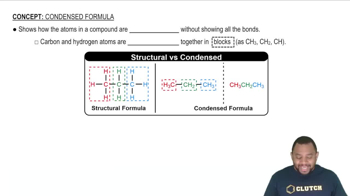
Draw the condensed structural formula for the alcohol formed when each of the following is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst:
a. butyraldehyde
Draw the condensed structural formula for the alcohol formed when each of the following is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst:
c. hexanal
Draw the condensed structural formula for the alcohol formed when each of the following is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst:
d. 2-methyl-3-pentanone
Draw the condensed structural formula for the alcohol formed when each of the following is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst:
c. 3-chlorocyclopentanone
Oxybenzone is an effective sunscreen whose structural formula is shown.
b. What is the molecular formula and molar mass of oxybenzone?
Avobenzone is a common ingredient in sunscreen. Its structural formula is shown.
a. What functional groups are in avobenzone?