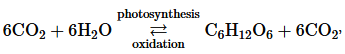Back
BackProblem 2a
The overall equation in this section,
shows the cycle between photosynthesis and oxidation. Pathways operating in opposite directions cannot be exergonic in both directions.
a. Which of the two pathways in this cycle is exergonic and which is endergonic?
Problem 4
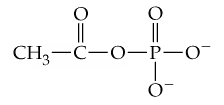
Acetyl phosphate, whose structure is given here, is another compound with a relatively high free energy of hydrolysis.
Using structural formulas, write the equation for the hydrolysis of this phosphate.
Problem 5
A common metabolic strategy is the lack of reactivity—that is, the slowness to react—of compounds whose breakdown is exergonic. For example, hydrolysis of ATP to ADP or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) is exergonic but does not take place without an appropriate enzyme present. Why would the cell use this metabolic strategy?
Problem 6
One of the steps in lipid metabolism is the reaction of glycerol (1,2,3-propanetriol, HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH, with ATP to yield glycerol 1-phosphate. Write the equation for this reaction using the curved arrow symbolism.
Problem 8
The hydrolysis of acetyl phosphate to give acetate and hydrogen phosphate ion has ∆G = -10.3 kcal/mol (-43.1 kJ/mol). Combine the equations and ∆G values to determine whether coupling of this reaction with phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP is favorable. (You need give only compound names or abbreviations in the equations.)