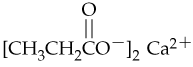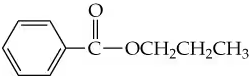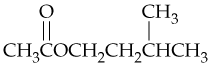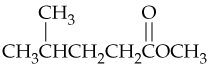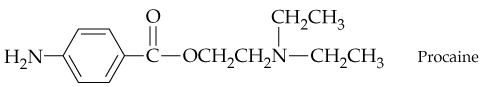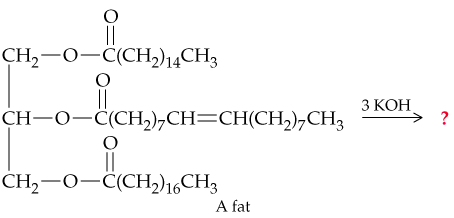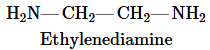Back
BackProblem 43d
Give systematic names for the following carboxylic acids:
d. CH3(CH2)5COOH
Problem 44a
Give systematic names for the following carboxylic acid salts:
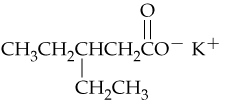
a.
Problem 44b
Give systematic names for the following carboxylic acid salts:
c.
Problem 47c
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
c. 3,3-Dimethyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid
Problem 49
Fumaric acid is a metabolic intermediate that has the systematic name trans-2-butenedioic acid. Draw its structure.
Problem 50
What is the formula for the diammonium salt of fumaric acid?
Problem 54d
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
d. Phenyl-o-hydroxybenzoate
Problem 55b
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
b. Ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate
Problem 55c
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
c.
Problem 56
Draw structures of the carboxylic acids and alcohols you would use to prepare each ester in Problem 17.54.
a.
b.
c. Cyclohexyl acetate
d. Phenyl-o-hydroxybenzoate
Problem 58c
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
c. N-Ethyl-N-methylbenzamide
Problem 59a
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
a. 3-Methylpentanamide
Problem 59b
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
b. N-Phenylacetamide
Problem 62
Procaine, a local anesthetic whose hydrochloride is Novocain, has the following structure. Identify the functional groups present, and show the structures of the alcohol and carboxylic acids you would use to prepare procaine.
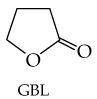
Problem 64
Lactones are cyclic esters in which the carboxylic acid part and the alcohol part are connected to form a ring. One of the most notorious lactones is gamma-butyrolactone (GBL), whose hydrolysis product is the 'date-rape' drug GHB. Draw the structure of GHB.
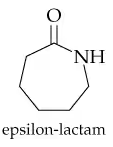
Problem 65a
When both the carboxylic acid and the amine are in the same molecule, amide formation produces lactams. A lactam is a cyclic amide, where the amide group is part of the ring. Draw the structure of the product(s) obtained from acid hydrolysis of these lactams.
a.
Problem 67b
Household soap is a mixture of the sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids that arise from saponification of animal fat.
b. Draw the structures of the soap molecules produced in the following reaction:
Problem 69
A simple polyamide can be made from ethylenediamine and oxalic acid (Table 17.1). Draw the polymer formed when three units of ethylenediamine reacts with two units of oxalic acid.
Problem 71a
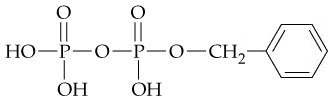
In the following compound
a. Identify the phosphate ester linkage.
Problem 71b
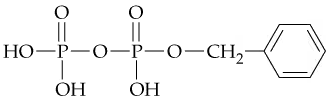
In the following compound
b. Identify the phosphate anhydride linkage.
Problem 74
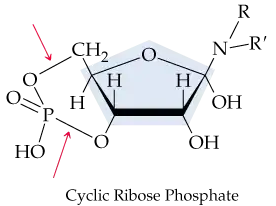
Cyclic ribose nucleotide phosphates, such as cyclic AMP (cAMP), are important signaling agents in living cells; all have the general structure shown here. What kind of linkage holds the phosphate to the ribose (see arrows; ribose is highlighted in blue)?
Problem 75
What is the difference between a phosphate diester and an ester of a diphosphate? Give an example of each.
Problem 78
Propanamide and methyl acetate have about the same molar mass, both are quite soluble in water, and yet the boiling point of propanamide is 213 °C, whereas that of methyl acetate is 57 °C. Explain.
Problem 79
Mention at least two simple chemical tests by which you can distinguish between benzaldehyde and benzoic acid.
Problem 80
Write the formula of the triester formed from glycerol and stearic acid.
Problem 82a
Each of the following materials has an ester that is responsible for its smell and/or flavor. Search the internet and determine what that ester is, draw its structure, and what carboxylic acid and alcohol are used to form it.
a. Juicy Fruit gum flavoring
Problem 83
Draw all possible carboxylic acids with the formula C5H10O2.