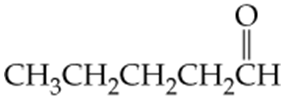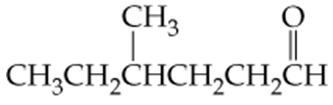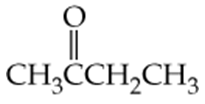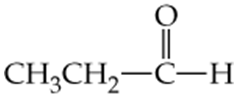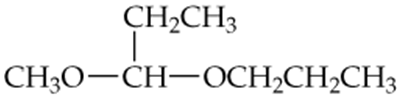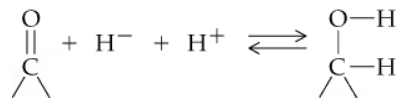Back
BackProblem 1
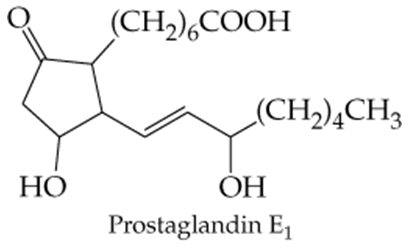
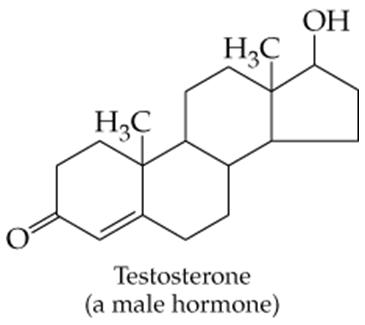
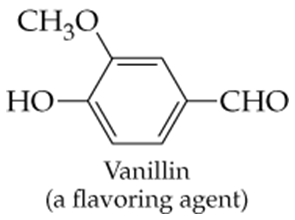
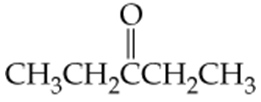
Which of the following molecules contain aldehyde or ketone functional groups? You may want to refer to Table 15.1, Table 12.1, and Figure 15.3 to help in your identification. Copy the formulas and circle these functional groups.
a.
b.
c.
d. C4H9COCH3
e. C4H9CHO
Problem 3
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
a. Octanal
b. Methyl phenyl ketone
c. 4-Methylhexanal
d. Methyl tert-butyl ketone
Problem 4
Give systematic, IUPAC names for the following compounds. Redraw each in line structure format.
a.
b.
c.
d. Dipropyl ketone
Problem 7
For each compound shown next (a–d), indicate whether the compound is polar or nonpolar, and whether it is soluble or insoluble in water.
a.
b.
c. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
d.
Problem 8
Why do aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling points than alcohols with similar molecular weights? Why are their boiling points higher than those of alkanes with similar molecular weights?
Problem 12
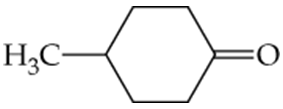
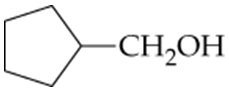
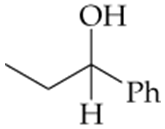
What ketones or aldehydes might be reduced to yield the following alcohols?
a.
b.
c. HOCH2–CH2–CH2OH
Problem 14c
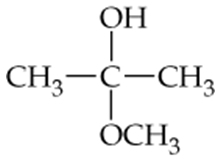
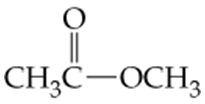
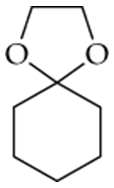
Determine whether the following compounds are acetals or ketals. Draw the structure of the aldehyde or ketone it came from.
c.
Problem 15b
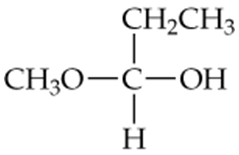
Draw the structures of the hemiacetals or hemiketals formed in these reactions:
b.
Problem 15.48
Aldosterone is a key steroid involved in controlling the sodium–potassium balance in the body. Identify the functional groups in aldosterone. <IMAGE>
Problem 17
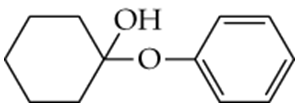
For each compound shown next, determine whether it is a hemiacetal, a hemiketal, an acetal, or a ketal.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Problem 20a
The carbonyl group can be reduced by addition of a hydride ion (H–) and (H+) a proton. Removal of H– and H+ from an alcohol results in a carbonyl group.
a. To which atom of the carbonyl is the hydride ion added and why?
Problem 20b
The carbonyl group can be reduced by addition of a hydride ion (H–) and (H+) a proton. Removal of H– and H+ from an alcohol results in a carbonyl group.
b. In the reaction, indicate which direction represents reduction and which represents oxidation.
Problem 21
A fundamental difference between aldehydes and ketones is that one can be oxidized to carboxylic acids but the other cannot. Which is which? Give an example of a test to differentiate aldehydes from ketones.
Problem 24
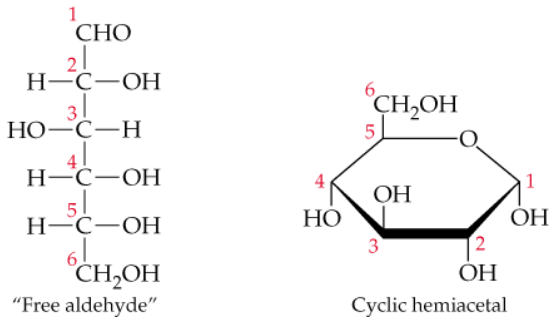
Glucose is the major sugar in mammalian blood. We often see it represented as either the "free aldehyde" or the cyclic hemiacetal forms shown here. Of the two forms of glucose, the cyclic hemiacetal is the preferred form found in blood. Can you suggest two reasons why?
Problem 26a
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
a. A 6-carbon cyclic ketone with a methyl group on the beta carbon